> Medicine Group. 2021 Apr 16;2(4):280-285. doi: 10.37871/jbres1225.
Phytochemical Analysis and Anticancer Activity of Azadirachta Indica Ethanolic Extract against A549 Human Lung Cancer Cell Line
Azhagu Madhavan S*
- Azadirachta indica
- Human cancer cell line A549
- Phytomedicine
Abstract
Azadirachta indica phytochemicals are found to have against malignant growth and hostile to bacterial properties. In the specific examination, the coupling proficiency of five mixes that are available in the Azadirachta indica with all the eleven proteins through in silico techniques was completed. Plant removes ensure against harmful compound instigated injury by expanding the body’s degrees of cell reinforcement particles, for example, glutathione, and improving the action of cancer prevention agent chemicals. A549 cells treated with Azadirachta indica ethanolic separate in various hours (6, 12, 24 and 36 hours) after the 36 hours the cells development are controlled. As there are re-established interests in home grown based meds to hinder the results of manufactured medications, Azadirachta Indica L. a leaf contains phytochemical intensifies having all the more free revolutionary rummaging just as anticancer exercises.
Introduction
Natural antibiotic properties of plant secondary metabolites
A local herb known as neem (semambu) or its logical name Azadirachta indica has been utilized widely in customary treatment because of its restorative properties. Neem leaves have been utilized generally for treating a few epidermal dysfunctions, for example, skin inflammation, psoriasis, and skin break out [1]. In the particular assessment, the coupling viability of five blends that are accessible in the Acalypha indica with all the eleven proteins through in silico procedures was finished. Gas Chromatography (GC) and Mass Spectrometry (MS) make a successful blend for synthetic investigation. Gas Chromatography (GC) is perhaps the most broadly utilized methods [2-5]. Thus, an endeavor has been made to assess the productivity of different natural solvents, antibacterial movement and distinguish the substance [6,7]. Segments by GC-MS investigation of rough bark separates from the Azadirachta indica against chose bacterial strains [8-11]. Neem is wealthy in cancer prevention agents and assists with boosting invulnerable reaction in tissues of influenced skin region [12-17]. It likewise comprises of bioactive mixes for antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer exercises [18]. In this investigation, neem leaves remove was utilized in creating natural neem cleanser as a solution for restoring skin issues (Figure 1).
Phytochemicals shows antioxidant activities
The free revolutionary present during our body are responsible for the age of numerous illnesses. One can keep himself from the illnesses create by activity of free extremists simply by deactivation of free revolutionary [19]. Cancer prevention agents have property to stop the movement of free extremists before its activity to words the organic cell of human body [20-23]. It has been accounted for that the oil ether, methanol and watery concentrates of the leaves of Azadirachta indica were screened for their enemy of microbial movement utilizing the cup plate agar dissemination technique [24,25]. They were tried against six microscopic organisms; two Grampositive microorganisms (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) and four Gram-negative microbes (Escherichia coli, Proteusvulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhi) [26-29]. The powerlessness of the microorganisms to the concentrates of this plant was contrasted and one another and with chose anti-infection agents [30]. The methanol concentrate of Azadirachta indica showed articulated movement against Bacillus subtilis (28mm). Azadirachta indica has a place with the family Meliaceae generally called as Neem (English), Vempu (Tamil) and is found all through India [31]. A medium to enormous estimated tree, grow up to 50 feet (15 m) tall and live for 200 y it has been recommended that ethanol extricates from plants utilized.
Activity against malaria
The antimalarial movements of the tablet suspension of the bark and leaf of Azadirachta indica were assessed. On Plasmodium yoelli nigeriensis contaminated mice [32]. “The tablet suspensions showed high prophylactic, moderate suppressive and a negligible therapeudic schizonticidal impact [33]. The tablet suspensions from the leaf and bark at a grouping of 800 mg/kg and chloroquine at a centralization of 62.5 mg/kg body weight delivered normal rate (%) parasitaemia of 79.6%, 68.2% and 99.5% for leaf, bark and chloroquine, individually, in chemosuppression. Likewise in the prophylactic treatment, the tablet suspensions at 800 mg/kg and pyrimethamine at a convergence of 0.35 mg/kg gave a normal parasitaemia decrease of 75.3%, 65.6% and 98.3% for the leaf, bark and pyrimethamine, individually [29]. Convenient was sign of reasonable valuable impact. In the only remaining century, huge advancement in bio-clinical science has vanquished numerous sicknesses anyway disease stays vague particularly from a restorative viewpoint [34]. Malignancy is as yet the most widely recognized reason for death from sickness after myocardial dead tissue. Tumor or neoplasm is generally characterized as a development of an irregular mass of tissue because of uncontrolled cell development, while disease is the term of every single dangerous tumor [27]. Numerous logical investigations that zeroed in on the pharmacological action of bio-dynamic parts from plants lately increment the premium from academic local area to distinguish some novel diseases suppressant. Natural focuses of phytochemicals in mammalian cells were found to metastases [22]. Also, epidemiological examinations recommend that the day by day admission of specific phytochemicals can lessen the frequency of a few sorts of malignant growths [17]. The primary framework in the body for breathing is respiratory framework. The respiratory framework incorporates the nose, mouth, (windpipe) and aviation routes to every lung. The aviation routes to every lung are called huge aviation routes (bronchi) and little aviation routes (bronchioles). Cellular breakdown in the lungs is the second most regular disease in the two people on the planet. It represents about 14% of all new diseases in the two people. For smokers the danger of cellular breakdown in the lungs is a lot higher than in non-smokers [11]. Cellular breakdown in the lungs is a malignancy that begins in the lungs. Cellular breakdowns in the lungs are thought to create over numerous years. There are 2 significant sorts of cellular breakdown in the lungs. On the off chance that a cellular breakdown in the lungs has qualities of the two sorts it is known as a blended little cell/huge cell malignancy this isn’t normal. Uranium is principle malignancy causing specialist found in rocks and soil [13]. As it rots, a gas called radon is freed and gets blended into air and water. Diggers of uranium have high danger of creating cellular breakdown in the lungs. A few investigations of radon found in the home have indicated its impact in causing cellular breakdown in the lungs, while different examinations have not. The danger for cellular breakdown in the lungs may rely upon how much level of radon gets presented to a person. The plant fabricated materials are appointed fundamental or discretionary metabolites [19]. Fundamental metabolites are extensively passed on in nature, occurring in some design in essentially all living creatures. In higher plants such blends are as often as possible stuffed in seeds and vegetative amassing organs and are needed for physiological headway considering their part in fundamental cell assimilation. Fundamental metabolites got from higher plants for business use are high volume-low worth mass manufactured mixes (for instance vegetable oils, unsaturated fats, starches, etc).
Material and Methods
Plant collection
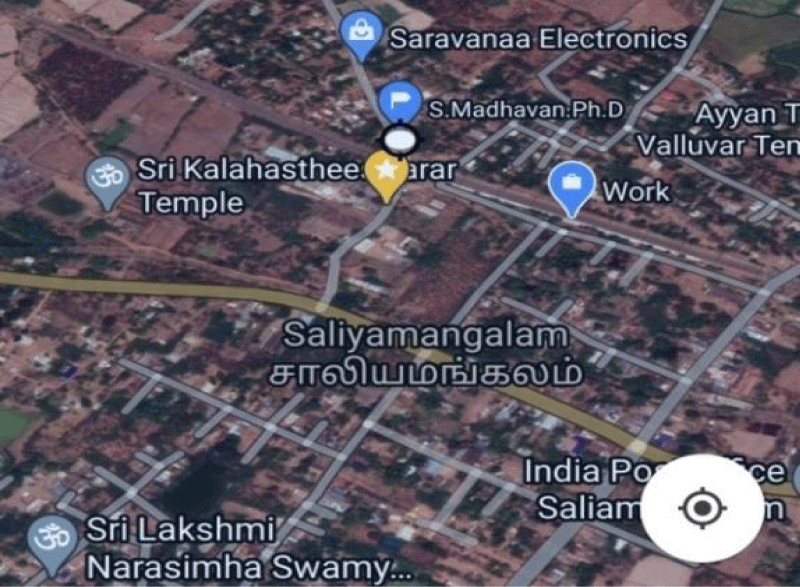
The fresh leaves of Azadirachta indica were collected from Saliyamangalam, Thanjavur District, Tamil Nadu, India (Figures 2 & 3).
Plant material
The Azadirachta indica leaves was dried up under shade, specifically diminish to a decently crude powder, and put away in golden hued sealed shut holders. The crude type of the medication was utilize for the declaration of physicochemical boundaries similar to dampness content, debris esteems, expanding file, frothing record, unfamiliar natural issue, extractive qualities, and fluorescence analysis.
Phytochemical studies
Secondary metabolites in the present studies were carried out on the plant sample revealed the presence of medicinally active constituents. Beneficial drugs and to improve the patient health.
Preparation of extracts
The powdered plant samples of leaves (100 g) were used for successive solvent extraction (500 ml) with increasing order of polarities like ethanol, methanol. At that point it is kept in an orbital shaker at 190-220 rpm for 48 hours. The supernatant was collected, filtered through Whatman No.1filter paper and the extract were concentrated by a Rotary flask evaporator at a specific temperature was used based on the solvent system. Each time previous to extract through the next solvent the remains was dried thoroughly to remove the solvent used. The acquired dried concentrate was then precisely gauged, put away in little vials at - 20°C and utilized for the accompanying examinations.
Phytochemical screening
The preliminary phytochemical evaluation was accepted out by using standard procedure [8,9].
Culturing of cell lines
The Vero and human lung cancer cells (A549) were obtained from Kings Institute of Preventive Medicine and Research, Guindy, Chennai. The cells were grown in 96-well Tissue Culture (TC) plate in Dulbecco’s Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) with Trypsin-Phosphate-Verseneglucose (TPVG) solution, 10% New Born Calf Serum (NBCS) (Gibco-Invitrogen), 100 U/mL of penicillin (Gibco-Invitrogen) and 100 mg/mL of streptomycin (Gibco-Invitrogen). The cells were incubated in CO2 incubator (Haier Electric Co., Ltd.,) at 37°C in 95% humidified atmosphere enriched by 5% CO2 and sub-cultured every 3-4 days once.
MTT cell viability assays
The MTT assay was done using the methodology of monolayer of cell culture was trypsinized and the cell count was adjusted to 1.0x105 cells/ml using growth medium. To each well of the 96 well microtitre plate, 0.1ml of the diluted cell suspension (approximately10, 000 cells /well) was added. After 24 hours, when a partial monolayer was formed, the supernatant was flicked off, the monolayer was washed once and 100 µl of leaves of Azadirachta indica leaves ethanolic extract with different concentrations (100, 200, 250, 500 and 1000 μg/ml) was added to each well. The plates were then incubated at 37°C for 3 days in 5% CO2 atmosphere, and microscopically examined at the end of 6, 12, 24 and 36 hours for recording the result. After 72 hours, the test solutions in the wells were discarded and 50 µl of MTT in HBSS-PR was added to each well. The plates were gently shaken and incubated for 3 hours at 37°C in 5% CO2 atmosphere. The supernatant was removed and 50 µl of propanol was added and therefore the plates were gently shaken to solubilize the formed formazan. The absorbance was measured using a microplate reader at the wavelength of 540 nm. The percentage growth inhibition was calculated using the formula given below:
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed by one way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) using Software Package for the Social Science (SPSS) software package version 15.00. Results were expressed as Mean ± Standard Deviation for p values <0.05 were considered significant for analysis of percent inhibition of cell growth.
Results and Discussion
The plants and its derivatives may considered as good sources of natural phytochemicals for medicinal uses such as against cancer, diabetic mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, aging and other diseases related to radical mechanisms. Plant-derived phytochemical therapy may be helpful for various free radical mediated diseases. Determination of the natural phytochemicals and antimicrobial compounds will help to develop new drugs [35-37]. The result of the preliminary phytochemical analysis of this present study may give credence to its ethno medicinal tradition [18]. In medicine, it is used in hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycaemia, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and weight loss among others. It is also known to contain antimicrobial properties.
Preliminary phytochemical screening
India is most likely the greatest creator of restorative flavours on the planet [12]. While the mechanism of action possessed by tannins is by disrupting the worm’s negative ion body charge into positive ions (protonization), which then attract positive worm body proteins in the gastrointestinal tract, thus disrupting the metabolism and homeostasis of the worm’s body and required into secondary metabolites (Table 1).
| Table 1: Qualitative analysis of Phytochemicals analysis Azadirachta indica leaves extract. | |||
| S. No | Analysed Phytochemicals factor |
Ethanol | Methanol |
| 1. | Tannin | ++ | + |
| 2. | Phlobatannins | - | + |
| 3. | Saponin | + | + |
| 4. | Flavonoids | ++ | + |
| 5. | Steroids | ++ | - |
| 6. | Terpenoids | + | + |
| 7. | Triterpenoids | + | + |
| 8. | Alkaloids | ++ | + |
| 9. | Carbohydrate | + | - |
| 10. | Protein | ++ | - |
| 11. | Anthraquinone | - | - |
| 12. | Polyphenol | ++ | + |
| 13. | Glycoside | + | - |
| Indications: “+” means positive activity, “-” means negative activity. | |||
A natural cleanser has been delivered effectively from neem leaves separate in this examination. The outcomes from the physicochemical properties of the neem cleanser arranged were contrasted with neem seed oil cleanser and business neem cleanser. The outcomes suggest that the neem cleanser created is reasonable for human skin. In addition, it is an item advancement of a characteristic sedated cleanser created from neem leaves remove that is liberated from synthetic substances, for example, Sodium Sulfate (SLS), fake colorant, and fake scent, hence can be a reasonable elective treatment for buyers who have skin issues [15]. However, there are numerous reports on the in vitro investigation of these mixes and its restorative and harmful properties, there are no in silico examines that foresee the authoritative and dynamic districts particularly with these proteins [6]. Our investigation is an endeavour to anticipate the coupling site and the coupling deposits. Nonetheless, approval of our outcomes through in vivo and in vitro tests and furthermore with creature models will edify trust for the future improvement of additional powerful medications for the treating of pharmacological significance of contain the properties, for example, antibacterial enemy of diabetic and pain relieving.
Anticancer activity on A549 cell lines
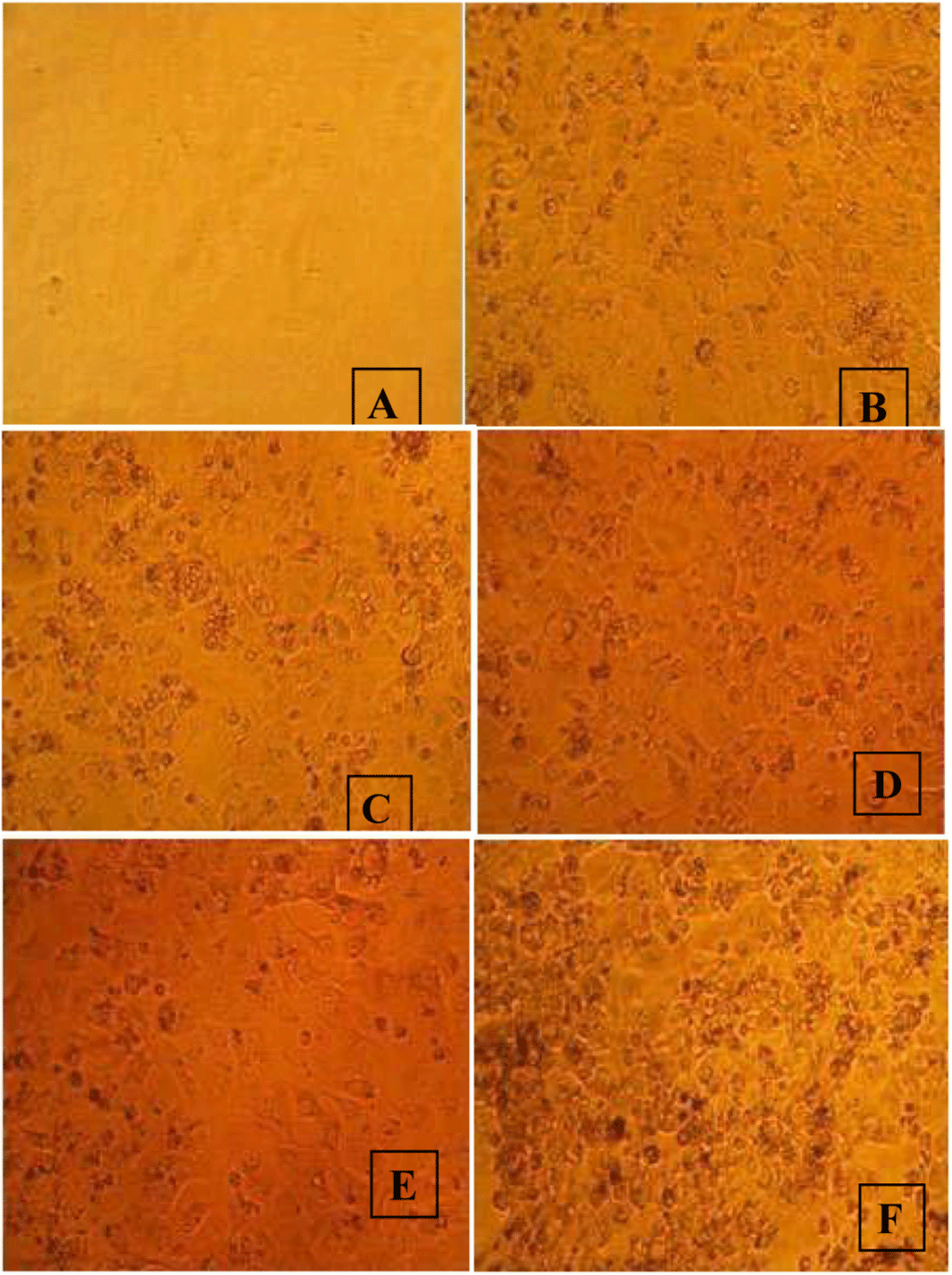
The Azadirachta indica ethanolic extract showed the anticancer activity against A549 cell line in a dose dependant manner. A549 cells treated with Azadirachta indica ethanolic extract in different hours (6, 12, 24 and 36 hours) after the 36 hours the cells growth are controlled. The Azadirachta indica ethanolic extract showed a maximum inhibition of 68% at 500 μg/ml against A549 lung cancer cells [11]. The present investigation the minimum inhibition of 12% was recorded at 100 μg/ml concentration. A549 cell normally contain a polygonal shape and expanse similar [9]. The Azadirachta indica ethanolic extract showed a maximum inhibition of 68% at 500 μg/ml against A549 lung cancer cells. The present investigation the minimum inhibition of 12% was recorded at 50 μg/ml concentration. Herbal mediated silver nanoparticles playing important role to create recyclable, cost effective and stable nanoparticles [12]. The investigates on union of silver nanoparticles utilizing different plant removes found that it is supplementary secure and better in malignant growth treatment, however more plants are as yet not investigated for the combination of nanoparticles and its applications of ethanolic commercial drug in cell restore 1000 µg/ml businesses.
Cell line image: A: Control; B: 100 μg/ml; C: 200 μg/ml; D: 250 μg/ml; E: 500 μg/ml; F: 1000 μg/ml
The cells of living beings can be considered as miniature synthetic reactors creating huge number of substance mixes through metabolic responses. Ayurvedic arrangement of medication in India and is utilized in relieving different sicknesses like stomach issues, gastric ulcers and to animate craving [14]. The cytotoxic properties were assessed, on Malignant growth cells of Breast cancer (MCF-7), cellular breakdown in the lungs (A-549) cell lines and contrast and ordinary cell line L-6 (Rat, Normal muscle) utilizing MTT colorimetric test for 24, 48 and 72 hrs. There is no orderly work that has been embraced on this plant and this is the principal report of the phytochemical screening, cell reinforcement and anticancer exercises evoked by saponin from Decalepis hamiltonii [14]. Combination of home grown intervened silver nanoparticles gives controlled and focusing on activity of medication, which can likewise defeat the issues related with traditional disease medicines [38]. The current investigation has been detailed to comprehend the phytochemical screening, in vitro cell reinforcement and anticancer properties evoked by saponin from foundations of Decalepis hamiltonii.
Conclusion
Allopathic medicine is potential sources of antiviral, antitumor and antimicrobial agents. The plausible instrument in cause the phone demise or apoptosis is by interfacing with the phone film proteins and making the phone release its constituents lastly driving passing or possibly it can connect with the DNA or cell declining pathways and controlling the pathways driving or scenery off the cell demise pathways. The presence of such assortment of phytochemicals might be credited to the therapeutic qualities of this plant Azadirachta indica. The consequences of this investigation uphold the conventional utilization of Azadirachta indica bark as an antibacterial specialist. In a few reports, these mixes can be answerable for the preventative properties credited to this plant in famous and conventional medication.
Acknowledgement
The author is also very grateful to the Secretary and Correspondent and the Principal of A.V.V.M. Sri Pushpam College (Autonomous), Poondi-613 503, Thanjavur (Dt), for providing the excellent infrastructure and necessary facilities to carry out my research work successfully.
References
- Zong A, Cao H, Wang F. Anticancer polysaccharides from natural resources: a review of recent research. Carbohydr Polym. 2012 Nov 6;90(4):1395-410. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.026. Epub 2012 Jul 16. PMID: 22944395.
- Efferth T, Koch E. Complex interactions between phytochemicals. The multi-target therapeutic concept of phytotherapy. Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Jan;12(1):122-32. doi: 10.2174/138945011793591626. PMID: 20735354.
- Mohan S, Dinakar S, Anand T, Elayaraja R, SathiyaPriya B. Phytochemical, GC-MS analysis and antibacterial activity of a medicinal plant acalypha indica. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2012,4(3):1050-1054. https://tinyurl.com/hphycbds
- Dwivedi VD, Tripathi IP, Mishra SK. In silico evaluation of inhibitory potential of triterpenoids from azadirachta indica against therapeutic target of dengue virus, NS2B-NS3 protease. J Vector Borne Dis. 2016 Apr-Jun;53(2):156-61. PMID: 27353586.
- Meena MK, Singh N, Patni V. Determination of bioactive components of the leaves of cocculus hirsutus (L.) diels using GC-MS analysis. Int J Pharm Sci. 2014;6:327-329. https://tinyurl.com/9xcmrk8t
- Kawatu CB, Mongi J. Gc–ms analysis of bioactive compounds present in ethanolic leaf extracts acalypha indica. Pharmacon. 2013;81-85. https://tinyurl.com/3r583w2k
- Al Akeel R, Mateen A, Janardhan K, Gupta VC. Analysis of anti-bacterial and anti-oxidative activity of azadirachta indica bark using various solvents extracts. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017 Jan;24(1):11-14. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 6. PMID: 28053565; PMCID: PMC5198926.
- Mandokhail F, Jamil N, Riaz M, Masood Z, Ahmed S, Asif B, Sham Din, Noor G, Rehman N, Zahid S, Bano A, Dil Murad, Shakeel D, Mengal F. Study of physical; and chemical properties of local neem (azadirachta indica) soap with branded soaping relation to their impact on skin. Am Euras J Toxicol Sci. 2015;7(4):239-242. https://tinyurl.com/e6pw5d9u
- Francine U, Jeannette U, Pierre RJ. Assessment of antibacterial activity of neem plant (azadirachta indica) on staphylococcus aureus and escherichia. Journal of Medicinal Plants Studies. 2015;3(4):85-91. https://tinyurl.com/e32b2r9y
- Hossain MA, Toubi WA, Sabahi JN, Weli AM, Riyami QA. Identification and characterization of chemical compounds in different crude extracts from leaves of omani neem. Journal of Taibah University for Science. 2013;7:181–188. https://tinyurl.com/c9jyejty
- Krishnasamyet A, Sundaresan M, Velan P. Rapid phytosynthesis of nano-sized titanium using leaf extract of Azadirachta indica. International Journal of Chem Tech Research. 2015; 8(4): 2047-2052. https://tinyurl.com/u3zexxpj
- Lakshmi T, Krishnan V, Rajendran R, Madhusudhanan N. Azadirachta indica: A herbal panacea in dentistry - an update. Pharmacogn Rev. 2015 Jan-Jun;9(17):41-4. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.156337. PMID: 26009692; PMCID: PMC4441161.
- Mensah EE, Firempong CK. Chemical characteristics of toilet soap prepared from neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) seed oil. Asian J Plant Sci Res. 2011;1(4):1-7. https://tinyurl.com/pubt9e73
- Kumar SV, Kumar C, Vardhan A. Hepatoprotective activity of Acalypha indica Linn against thioacetamide-induced toxicity. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2013;5:3-6. https://tinyurl.com/ns54yxww
- Lee EJ, Oh H, Kang BG, Kang MK, Kim DY, Kim YH, Lee JY, Ji JG, Lim SS, Kang YH. Lipid-lowering effects of medium-chain triglyceride-enriched coconut oil in combination with licorice extracts in experimental hyperlipidemic mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Oct 10;66(40):10447-10457. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04080. Epub 2018 Oct 2. PMID: 30244576.
- Chekuri S, Panjala S, Anupalli RR. Cytotoxic activity of acalypha indica L. hexane extract on breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7). J Phytopharmacol. 2017;6(5):264-268. https://tinyurl.com/2wrtc47x
- Joshi SM, De Britto S, Jogaiah S, Ito SI. Mycogenic selenium nanoparticles as potential new generation broad spectrum antifungal molecules. Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 28;9(9):419. doi: 10.3390/biom9090419. PMID: 31466286; PMCID: PMC6769984.
- Asghari-Paskiabi F, Imani M, Rafii-Tabar H, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Physicochemical properties, antifungal activity and cytotoxicity of selenium sulfide nanoparticles green synthesized by saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Sep 3;516(4):1078-1084. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 4. PMID: 31280861.
- Menon S, Agarwal H, Rajeshkumar S, Rosy PJ, Shanmugam VK. Investigating the antimicrobial activities of the biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles and its statistical analysis. Bio Nano Science. 2020;10:122–135https://tinyurl.com/52wne4d2
- Menon S. Selenium nanoparticles: A potent chemotherapeutic agent and an elucidation of its mechanism. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 Oct 1;170:280-292. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jun 5. PMID: 29936381.
- Murugesan G, Nagaraj K, Sunmathi D, Subramani K. Methods involved in the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their different applications-a review. Eur J Biomed. 2019;6:189-194. https://tinyurl.com/4a4zprhs
- VR Marathe. Nutraceutical evaluation of acalypha indica l. - A potential wild edible plant. International Journal of Green Pharmacy. 2018;12(3 Suppl):510-517. https://tinyurl.com/3htzn8yj
- Teklani PWNN, Perera BGK. The important biological activities and phytochemistry of acalypha indica. International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science. 2016;6(1):30-35. https://tinyurl.com/stdfwx93
- Prem KK, Nirmala B, Rani AR. Antimicrobial, antioxidant activity and phytochemical screening of acalypha indica crude leaf extract. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2016;8(6):583-588. https://tinyurl.com/57vdsszy
- Nurul NMN, Norazlanshah H, Muhammad I, Mashita M, Ayob MK. Preliminary studies on acalypha indica: proximate analysis and phytochemical screening. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016;8(3):406-408. https://tinyurl.com/x8vfy7f7
- Chandrasekar R, Sivagami B. Alternative treatment for psoriasis - A review. International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences. 2016;5(4):2188-2197. https://bit.ly/3gpDm39
- Rajkiran Reddy Banala, Satish Kumar Vemuri, Gurava Reddy AV, Subbaiah GPV. Aqueous extract of Acalypha indica leaves for the treatment of Psoriasis: in-vitro studies. International Journal of Bioassays. 2017;6(4):5360-5364. https://bit.ly/2RyatXT
- Mohan C, Dinakar S, Anand T. Phytochemical, GC-MS analysis and antibacterial activity of a medicinal plant Acalypha indica. Int J PharmTech Res. 2012;4:1050-1054. https://bit.ly/2QsQ9Xy
- Eid A, Jaradat N, Elmarzugi N. A Review of chemical constituents and traditional usage of Neem plant (Azadirachta indica), Palest Med Pharm J. 2017;2:75-81.
- Ojewumi ME, Owolabi RU. The effectiveness of the extract of ‘Hyptis suaveolens’ leave (a specie of effinrin) in repelling mosquito. Transnatl J Sci Technol. 2012;2(8):79-87.
- Ogunlana OO, Ogunlana OE, Ntube CA, Olagunju JA. Akindahunsi AA. Phytochemical Screening and in vivo antioxidant activity of Ethanolic extract of caesalpinia bonduc (L.) Roxb Glob Res J Pharm Sci. 2012;1(1):1-4. https://bit.ly/3tnsuGm
- Pan SY. New perspectives on how to discover drugs from herbal medicines: CAM’s outstanding contribution to modern therapeutics, Evidence-Based Complement. Altern Med. 2013;1-25. https://bit.ly/3mWQ0YA
- Ojewumi ME, Adedokun SO, Omodara OJ. Oyeniyi EA, Taiwo OS, Ojewumi EO, Phytochemical and antimicrobial activities of the leaf oil extract of Mentha spicata and its efficacy in repelling mosquito. Int J Pharm Res Allied Sci. 2021;6(4);17-27. https://bit.ly/3dhIRif
- Babatunde DE, Otusemade GO, Ojewumi ME, Agboola KD, Akinlabu Oyeniyi E. Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical screening of neem leaves and lemon grass essential oil extracts, Int J Mech Eng Technol. 2019. https://bit.ly/2Qv8fI8
- Azhagu Madhavan S, Vinotha p, Uma V. Pharmacological and Anti-Cancer Activity of Ipomoea sepiaria Methanolic Extract against PC-3 Cell Line. Asian Journal of Advances in Medical Science. 2020;2(3):26-32. https://bit.ly/3tn69ZJ
- Azhagu Madhavan S, Mahadevi M, Vinotha P3, Uma V. Anti - HyperglycemiaActivity of Aloe Vera Ethanolic Extract against Mouse 3t3-L1 Adipocyte Cell Line. International Journal of Applied Chemical and Biological Sciences. 2020;1(3):58-66. https://bit.ly/2Q6c72v
- Azhagu Madhavan S, Vinotha P, Uma V, Mahadevi M. Anticancer Activity of Pedalium Murex Linn Methanolic Leaves Extract Against A549 Human Lung Cancer Cell Line. Asian Journal of Advances in Research. 2020;5(1):33-40. https://bit.ly/32gXewR
- Azhagu Madhavan S, Ganesan S. Phytochemicals Analysis of Anti-Diabetic Effect of Costus Spicatus in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar Male Rats. European Journal of Research Development and Sustainability (EJRDS). 2021;2(2). https://bit.ly/2RDsTqn
Content Alerts
SignUp to our
Content alerts.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.