> Medicine Group. 2021 May 22;2(5):372-378. doi: 10.37871/jbres1244.
Pharmacognostical and Phytochemical Screening of GC–MS Analysis of Bioactive Compounds Present in Ethanolic Rhizome Extract of Zingiber officinale Roscoe
Azhagu Madhavan S1*, Priyadharshini R1, Sripriya R1, Uma V2 and Vinotha P3
2Sri Sai Apollo Educational Insttute, Bio-Chemistry, Veppur- 60634, Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India
3PG & Research Department of Bio-Chemistry, Meenakshmi Chandrasekaran College of Arts and Science, Karambayam-614601, Pattukkottai, Thanjavur District, Tamil Nadu, India
- Zingiber officinale Rosc
- Ginger
- GC-MS Analysis
- Phytochemical
Abstract
Nowadays, nanotechnology is used as a way to increase bioavailability and decrease the side effects of drugs and nutrients. Micronutrients and nutraceuticals such as vitamins, carotenoids, polyunsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols are classes of food ingredients that are essential for human health and well-being. These compounds are rarely added purely to the targeted food application but rather in encapsulated, solid, dry product forms with added functionalities such as improved stability, bioavailability or handling. Development of new strategies, like nanocarriers, that help to promote the access of neuroprotective molecules to the brain, is needed for providing more effective therapies for the disorders of the Central Nervous System (CNS). Polymer–lipid hybrid nanoparticles, encapsulating vitamin D3 and vitamin K2, with improved features in terms of stability, loading and mucoadhesiveness were produced for potential nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications. Recently, nanoformulations that include nanovesicles, solid-lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers, nanoemulsions, and polymeric nanoparticles have shown promising outcomes in improving the efficacy and bioavailability of vitamin E. Active targeting of nanoparticles loaded with vitamin D to cancer cells.
Introduction
Phytopathogens are the primary driver of plant illnesses that bring about huge harvest misfortunes, particularly in jungles. Anticipation or decrease of plant infection invasion is a significant worry of ranchers. Notwithstanding the advances underway horticulture, powerful administration of plant infection stays a test on account of the results of existing pesticides as the majority of them artificially engineered (bactericides, fungicides, among others [1]. Goldmines as they contain normal synthetics, which are adequate to human and creature frameworks. Every one of these synthetic substances can’t be blended in labs. Numerous auxiliary metabolites of plant are industrially significant and discover use in various drug compounds [2]. Individuals have been reliant on plants for their medical services needs since the start of development [3]. The 2,50000 higher plant species on earth, more than 80,000 are restorative in Nature [4]. Ginger experimentally known as Zingiber officinale Roscoe, having a place with family Zingiberaceae is quite possibly the main plant with a few restorative, wholesome and ethanomedical values along these lines, utilized broadly worldwide as a zest, seasoning specialist and home grown cure [5]. Customarily, Z. officinale is utilized in Ayurveda, Siddha, Chinese, Arabian, Africans, Caribbean and numerous other restorative frameworks to fix an assortment of sicknesses viz, queasiness, regurgitating, asthma, hack, palpitation, aggravation, dyspepsia, loss of hunger, clogging, heartburn and torment Species from Zingiberaceae family have been generally utilized as flavours [6]. The expanded utilization of anti-infection agents has instigated microorganisms to procure opposition factors which have become a consuming situation. Red ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe var rubrum) has been developed because of its wide scope of corrective impacts. It is known as a fundamental creation of Indonesian society medication called Jamu [7]. Red ginger contains the most noteworthy fundamental oil among different variations of ginger planted in Indonesia, for example, Zingiber officinale Roscoe (regular ginger) and Zingiber officinale var. amarum (white little ginger) [8]. Ginger concentrate was set up from dried ginger and cancer prevention agents were improved utilizing dissolvable parcel [9]. Concentrates and portions were assessed for their cell reinforcement potential in various in vitro model frameworks. The arrangement of biofilm prompts protection from every antifungal class, bringing about the lone treatment being a medical procedure, to eliminate the tainted inserts. This is finished with a blend with high portions of antifungal medications [10]. Expulsion of inserts, for example, fake heart valves may expand the dangers in the patient’s condition and isn’t affordable. Besides, the utilization of high-portion antifungal medications can prompt liver and kidney harm [11]. Thus there is a pressing need to locate the option of chemotherapeutic medications in infections treatment especially those of plant birthplace which are effectively accessible and have significantly less results. The antimicrobial action of flavors is because of specific phytochemicals or fundamental oils present in ginger.
Material Methods
Plant collection
Fresh, healthy, and young rhizome of Zingiber officinale were collected from Laycowin Organic, Herbal and Medicinal Products, Thanjavur (10.7821° N, 79.2756° E), Tamilnadu, India.
Plant material
The Zingiber officinale rhizome was dried up under shade, specifically diminish to a decently crude powder, and put away in golden hued sealed shut holders. The crude type of the medication was utilize for the declaration of physicochemical boundaries similar to dampness content, debris esteems, increasing case, frothing evidence, unfamiliar natural issue, extractive qualities, and fluorescence analysis.
Phytochemical studies
Secondary metabolites in the present studies were carried out on the plant sample revealed the presence of medicinally active constituents. Beneficial drugs and to improve the patient health.
Preparation of extracts
The powdered plant samples of rhizome (100 g) were used for successive solvent extraction (500ml) with increasing order of polarities like ethanol, methanol. At that point it is kept in an orbital shaker at 190-220rpm for 48 hours. The supernatant was collected, filtered through Whatman No.1filter paper and the extract were concentrated by a Rotary flask evaporator at a specific temperature was used based on the solvent system. Each time previous to extract through the next solvent the remains was dried thoroughly to remove the solvent used. The acquired dried concentrate was then precisely gauged, put away in little vials at - 20°C and utilized for the accompanying examinations.
Phytochemical screening
The preliminary phytochemical evaluation was carried out by using standard procedure [12-15].
Gas Chromatography-Mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis
Clarus 500 Perkin- Elmer (Auto System XL) Gas Chromatograph equipped and coupled to a mass detector Turbo mass gold – Perking Elmer Turbomas 5.2 spectrometer with an Elite-1 (100% Dimethyl ply siloxane), 300 m x 0.25 mm x 1 μm df capillary column was used for GCMS analysis. Initially, the instrument was set to temperature of 110°C, and then maintained at the same temperature for 2 min. At the end of this period, the oven temperature was raised up to 280°C, at the rate of an increase of 5°C per minute and maintained for 9 min. The temperature of injection port was ensured as 250°C and the flow rate of Helium as 1 ml/min. The ionization voltage was 70 eV. The samples were injected gradually in split mode as 10:1. The range of mass spectrum was set at 45-450 (mhz). The chemical constituents were identified by GC-MS. The discontinuity examples of mass spectra were contrasted and those put away in the spectrometer information base utilizing National Institute of Standards and Technology Mass Spectral information base (NIST-MS). The percentage of each constituent was calculated from relation peak area of each component in the chromatogram.
Identification of Compounds
Translation of mass range of GC-MS was directed utilizing the information base of National Institute Standard and Technology (NIST) having in excess of 62,000 examples. The unknown component’s spectrum was compared with the spectrum of the known components stored in the NIST library. The structure, name and sub-atomic load of the parts of the test materials was learned.
Results and Discussion
The plants and its subsidiaries may considered as great wellsprings of characteristic phytochemicals for therapeutic uses, for example, against malignancy, diabetic mellitus, cardiovascular illnesses, maturing and different infections identified with extremist instruments. The consequence of the primer photochemical examination of this current investigation may offer trustworthiness to its ethno medicinal utilization.
Preliminary phytochemical screening
Saponin is utilized as a mellow cleanser and in intracellular his to science staining to permit immune response admittance to intracellular proteins. In medication, it is utilized in hyperchlolesterolaemia, hyperglycaemia, cell reinforcement, anticancer, calming, and weight reduction among others [16]. It is likewise known to have antimicrobial properties. India is in all probability the best maker of remedial flavors on the planet (Table 1).
| Table 1: Qualitative analysis of Phytochemicals analysis Zingiber officinale rhizome Extract. | |||
| S. No | Phytochemicals factor | Ethanol | Methanol |
| 1. | Tannin | ++ | + |
| 2. | Phlobatannins | + | + |
| 3. | Saponin | + | + |
| 4. | Flavonoids | ++ | + |
| 5. | Steroids | - | - |
| 6. | Terpenoids | + | + |
| 7. | Triterpenoids | + | + |
| 8. | Alkaloids | ++ | + |
| 9. | Carbohydrate | + | - |
| 10. | Protein | - | - |
| 11. | Anthraquinone | - | - |
| 12. | Polyphenol | ++ | + |
| 13. | Glycoside | + | - |
| Indications: “+” means positive activity, “-” means negative activity | |||
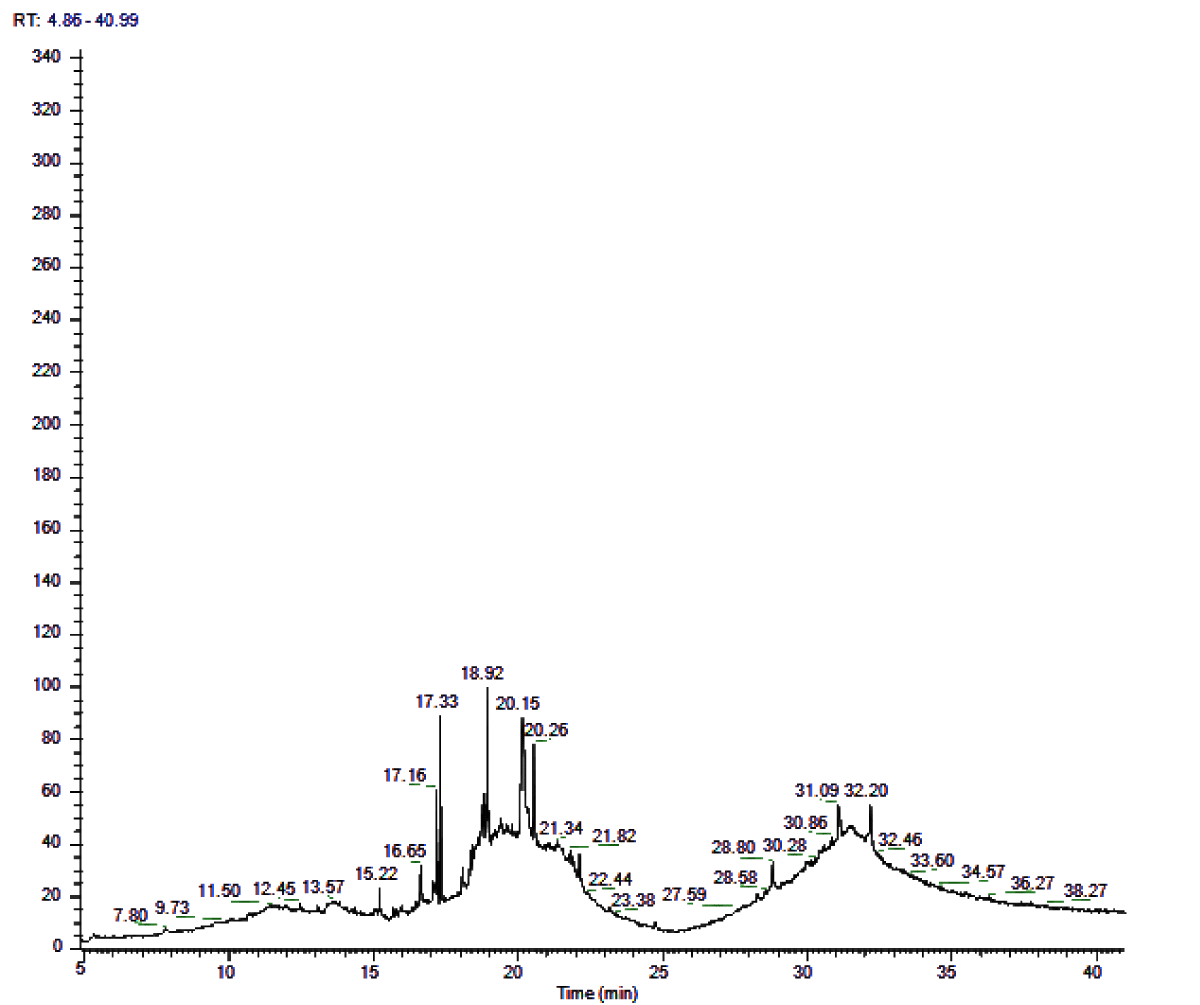
Each constituent assumes a significant part and lack of any one constituent may prompt unusual advancements in the body [17]. While the component of activity controlled by tannins is by upsetting the worm’s negative particle body surge into positive particles (protonization), which at that point pull in sure worm body proteins in the gastrointestinal parcel, accordingly disturbing the digestion and homeostasis of the worm’s body (Figure 1) (Tables 2, 3).
| Table 2: GCMS analysis - Bioactive compounds Zingiber officinale rhizome Ethanolic extract. | ||||||
| S.NO | Retention time | Compound name | Molecular formula | Molecular Weight | Area (%) | Structure |
| 1 | 15.22 | Octanal | C85H16O | 128 | 0.47 |  |
| 2 | 16.65 | Endo-Borneol | C10H18O | 154 | 0.188 | 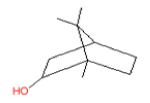 |
| 3 | 17.16 | Decanal | C10H20O | 156 | 0.602 | 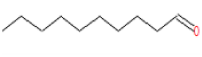 |
| 4 | 17.33 | 1,2-15,16- Diepoxyhexadecane | C16H30O2 | 254 | 1.072 | 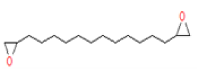 |
| 5 | 18.92 | Propanal,2- methyl-3-phenyl | C10H12O | 148 | 1.692 | 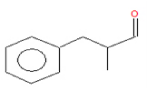 |
| 6 | 20.15 | Bicyclo[3.1.0] hexane-6-methanol, 2-hydroxy-1,4, 4-trimethyl | C10H18O2 | 170 | 3.15 | 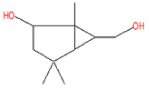 |
| 7 | 20.26 | 7-epi-cis- sesquisabinene hydrate | C15H26O | 222 | 1.59 | 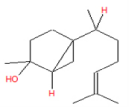 |
| 8 | 21.34 | Benzene,1- (1,5-dimethyl-4- hexenyl)-4-methyl | C15H22 | 202 | 0.07 | 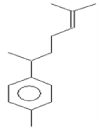 |
| 9 | 21.82 | Aromadendrene oxide | C15H24O | 220 | 0.12 | 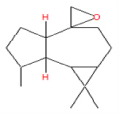 |
| 10 | 28.8 | 4-((1H)-3- Hydroxy-1- propenyl)-2 –methoxyphenol | C10H12O3 | 180 | 0.031 | 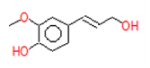 |
| 11 | 31.09 | 1b,4a-Epoxy- 2H-cyclopenta[3,4] cyclopropa[8,9] cycloundec[1,2-b]o | C22H32O8 | 424 | 0.47 | 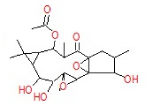 |
| 12 | 32.20 | 2-Methylcortisol | C22H32O5 | 376 | 0.52 | 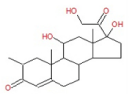 |
| Table 3: GCMS analysis - Bioactive compounds Zingiber officinale rhizome Biological Activity. | |||||
| S. No. | Retention time | Compound name | Molecular formula | Molecular Weight | Biological Activity |
| 1 | 15.22 | Octanal | C85H16O | 128 | Antioxidant activity and anti -inflammatory activities [18] |
| 2 | 16.65 | Endo-Borneol | C10H18O | 154 | Antinociceptive and anti- inflammatory activities |
| 3 | 17.16 | Decanal | C10H20O | 156 | Anti-Salmonella agents and antioxidant activity [19] |
| 4 | 17.33 | 1,2-15,16- Diepoxyhexadecane | C16H30O2 | 254 | Antitumor and anti-inflammatory agents |
| 5 | 18.92 | Propanal,2- methyl-3-phenyl | C10H12O | 148 | Various biological activities such as anti- inflammatory [20] |
| 6 | 20.15 | Bicyclo[3.1.0] hexane-6-methanol, 2-hydroxy-1,4, 4-trimethyl | C10H18O2 | 170 | Anti-Candida and anti-inflammatory |
| 7 | 20.26 | 7-epi-cis- sesquisabinene hydrate | C15H26O | 222 | Anti-cancer |
| 8 | 21.34 | Benzene,1- (1,5-dimethyl-4- hexenyl)-4-methyl | C15H22 | 202 | Antimicrobial and Anti- inflammatory |
| 9 | 21.82 | Aromadendrene oxide | C15H24O | 220 | Anti HIV5,6, antifungal and antimicrobial |
| 10 | 28.8 | 4-((1H)-3- Hydroxy-1- propenyl)-2 -methoxyphenol | C10H12O3 | 180 | Antioxidant, anti microbial and anti-inflammatory [21] |
| 11 | 31.09 | 1b,4a-Epoxy- 2H-cyclopenta[3,4] cyclopropa[8,9] cycloundec[1,2-b]o | C22H32O8 | 424 | - |
| 12 | 32.20 | 2-Methylcortisol | C22H32O5 | 376 | Anti-inflammatory [22] |
The current investigation express that the presence of methyl or ethyl esters of unsaturated fats can likewise be considered as qualities of this plant [23]. From this outcome, it very well may be reasoned that every one of these mixes are of pharmacological significance as they have the properties, for example, antibacterial enemy of diabetic and pain relieving.
Summary and Conclusion
The ginger oil contains a mixture of constituents such as monoterpenes, namely phellandrene, camphene, cineole, linalool, limonene, citral, geraniol, citronellol, borneol and sesquiterpenes, namely α-zingiberene, ar-curcumene, β-bisabolene, β-sesquiphellandrene, zingiberol and zingiberenol along with some aliphatic aldehydes and alcohols [24]. The composition of volatile oil is highly variable depending upon a variety of factors including their geographical origin, distillation procedures, post harvest treatment, processing, drying conditions and temperature [25]. The present communication, we report essential oil composition of the rhizomes of Z. officinale from Ghaziabad region and its antimicrobial activity. Today, looking towards the side effects of modern medicine, the invention of novel active compounds against new targets is a matter of urgent priority in drug discovery. From the results obtained in the present investigation, it could be concluded that Zingiber officinale possesses remarkable bioactive compounds having therapeutic effects and can be considered a potential source of medicinal herb. Zingiber officinale possesses remarkable antimicrobial activity, which is mainly due to naphthalenamine, decanal, and alfa.-copaene. According to these findings, it could be said that the ethanolic extract act as antibacterial agents.
Acknowledgement
The ginger oil contains a mixture of constituents such as monoterpenes, namely phellandrene, camphene, cineole, linalool, limonene, citral, geraniol, citronellol, borneol and sesquiterpenes, namely α-zingiberene, ar-curcumene, β-bisabolene, β-sesquiphellandrene, zingiberol and zingiberenol along with some aliphatic aldehydes and alcohols [24]. The composition of volatile oil is highly variable depending upon a variety of factors including their geographical origin, distillation procedures, post harvest treatment, processing, drying conditions and temperature [25]. The present communication, we report essential oil composition of the rhizomes of Z. officinale from Ghaziabad region and its antimicrobial activity. Today, looking towards the side effects of modern medicine, the invention of novel active compounds against new targets is a matter of urgent priority in drug discovery. From the results obtained in the present investigation, it could be concluded that Zingiber officinale possesses remarkable bioactive compounds having therapeutic effects and can be considered a potential source of medicinal herb. Zingiber officinale possesses remarkable antimicrobial activity, which is mainly due to naphthalenamine, decanal, and alfa.-copaene. According to these findings, it could be said that the ethanolic extract act as antibacterial agents.
References
- Casmir. The journal of State Medicine. Volume XX: 341-368, 1912. The etiology of the deficiency diseases, Beri-beri, polyneuritis in birds, epidemic dropsy, scurvy, experimental scurvy in animals, infantile scurvy, ship beri-beri, pellagra. Nutr Rev. 1975 Jun;33(6):176-177. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1975.tb05095.x. PMID: 1095967.
- Gonnet M, Thuaut, Boury F. New trends in encapsulation of liposoluble vitamins. Journal of Controlled Release,. 2010;146:276-290.
- Fang Z, Bhandari B. Encapsulation of polyphenols - A review. Trends in Food Science and Technology. 2010;21:510-523. https://tinyurl.com/nvtp25yz
- Munin A, Edwards-Lévy F. Encapsulation of natural polyphenolic compounds: A review. Pharmaceutics. 2011 Nov 4;3(4):793-829. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics3040793. PMID: 24309309; PMCID: PMC3857059.
- Khalifa SAM, Elias N, Farag MA, Chen L, Saeed A, Hegazy MF, Moustafa MS, Abd El-Wahed A, Al-Mousawi SM, Musharraf SG, Chang FR, Iwasaki A, Suenaga K, Alajlani M, Göransson U, El-Seedi HR. Marine natural products: A source of novel anticancer drugs. Mar Drugs. 2019 Aug 23;17(9):491. doi: 10.3390/md17090491. PMID: 31443597; PMCID: PMC6780632.
- Pandey N, Meena RP, Rai SK, Pandey S. Medicinal Plants Derived Nutraceuticals: A ReEmerging Health Aid. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. 2011;2:.419-441.
- Zhang Y, Zhou WE, Yan JQ, Liu M, Zhou Y, Shen X, Ma YL, Feng XS, Yang J, Li GH. A Review of the Extraction and Determination Methods of Thirteen Essential Vitamins to the Human Body: An Update from 2010. Molecules. 2018 Jun 19;23(6):1484. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061484. PMID: 29921801; PMCID: PMC6099991.
- Eggersdorfer M, Laudert D, Létinois U, McClymont T, Medlock J, Netscher T, Bonrath W. One hundred years of vitamins-a success story of the natural sciences. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012 Dec 21;51(52):12960-12990. doi: 10.1002/anie.201205886. Epub 2012 Dec 3. PMID: 23208776.
- Karaźniewicz-Łada M, Główka A. A review of chromatographic methods for the determination of water- and fat-soluble vitamins in biological fluids. J Sep Sci. 2016 Jan;39(1):132-148. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201501038. Epub 2015 Nov 25. PMID: 26503668.
- Weber D, Grune T. The contribution of β-carotene to vitamin A supply of humans. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 Feb;56(2):251-258. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100230. Epub 2011 Sep 29. PMID: 21957049.
- Jacob RA, Sotoudeh G. Vitamin C function and status in chronic disease. Nutr Clin Care. 2002 Mar-Apr;5(2):66-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x. PMID: 12134712.
- Wimalawansa SJ. Vitamin D in the new millennium. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2012 Mar;10(1):4-15. doi: 10.1007/s11914-011-0094-8. PMID: 22249582.
- Bouillon R, Suda T. Vitamin D: Calcium and bone homeostasis during evolution. Bonekey Rep. 2014 Jan 8;3:480. doi: 10.1038/bonekey.2013.214. PMID: 24466411; PMCID: PMC3899559.
- Sen CK, Khanna S, Roy S. Tocotrienols: Vitamin E beyond tocopherols. Life Sci. 2006 Mar 27;78(18):2088-2098. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.12.001. Epub 2006 Feb 3. PMID: 16458936; PMCID: PMC1790869.
- Shearer MJ, Okano T. Key pathways and regulators of vitamin k function and intermediary metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 2018 Aug 21;38:127-151. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-082117-051741. Epub 2018 Jun 1. PMID: 29856932.
- Holick MF. The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2017 Jun;18(2):153-165. doi: 10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1. PMID: 28516265.
- Dobnig H. A review of the health consequences of the vitamin D deficiency pandemic. J Neurol Sci. 2011 Dec 15;311(1-2):15-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2011.08.046. Epub 2011 Sep 22. PMID: 21939984.
- Rice ME. Ascorbate regulation and its neuroprotective role in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 2000 May;23(5):209-16. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01543-x. PMID: 10782126.
- Harrison FE, Bowman GL, Polidori MC. Ascorbic acid and the brain: rationale for the use against cognitive decline. Nutrients. 2014 Apr 24;6(4):1752-81. doi: 10.3390/nu6041752. PMID: 24763117; PMCID: PMC4011065.
- Rebec GV, Pierce RC. A vitamin as neuromodulator: ascorbate release into the extracellular fluid of the brain regulates dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission. Prog Neurobiol. 1994 Aug;43(6):537-65. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90052-3. PMID: 7816935.
- Rebec G.V, Barton SJ, Marseilles AM, Collins K. Ascorbate treatment attenuates the huntington behavioral phenotype in mice. Neuroreport. 2003;14:1263–1265. doi: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000081868.45938.12
- Qiu S, Li L, Weeber EJ, May JM. Ascorbate transport by primary cultured neurons and its role in neuronal function and protection against excitotoxicity. J Neurosci Res. 2007 Apr;85(5):1046-1056. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21204. PMID: 17304569.
- Ballaz S, Morales I, Rodríguez M, Obeso JA. Ascorbate prevents cell death from prolonged exposure to glutamate in an in vitro model of human dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2013 Dec;91(12):1609-1617. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23276. Epub 2013 Aug 30. PMID: 23996657.
- Mocchegiani E, Costarelli L, Giacconi R, Malavolta M, Basso A, Piacenza F, Ostan R, Cevenini E, Gonos ES, Franceschi C, Monti D. Vitamin E-gene interactions in aging and inflammatory age-related diseases: implications for treatment. A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2014 Mar;14:81-101. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 11. PMID: 24418256.
- Crouzin N, Ferreira MC, Cohen-Solal C, Barbanel G, Guiramand J, Vignes M. Neuroprotection induced by vitamin E against oxidative stress in hippocampal neurons: involvement of TRPV1 channels. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010 Apr;54(4):496-505. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900188. PMID: 20087852.
- Dolu N, Khan A, Dokutan Ş. Effect of Vitamin E Administration on Learning of the Young Male Rats. J Exp Neurosci. 2015 Sep 2;9:81-85. doi: 10.4137/JEN.S29843. PMID: 26380558; PMCID: PMC4559183.
- Harrison FE, May JM. Vitamin C function in the brain: vital role of the ascorbate transporter SVCT2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Mar 15;46(6):719-730. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.12.018. Epub 2009 Jan 6. PMID: 19162177; PMCID: PMC2649700.
- Kontush A, Mann U, Arlt S, Ujeyl A, Lührs C, Müller-Thomsen T, Beisiegel U. Influence of vitamin E and C supplementation on lipoprotein oxidation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001 Aug 1;31(3):345-354. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(01)00595-0. PMID: 11461772.
- Manor D, Morley S. The alpha-tocopherol transfer protein. Vitam Horm. 2007;76:45-65. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(07)76003-X. PMID: 17628171.
- Spector R, Johanson CE. Vitamin transport and homeostasis in mammalian brain: focus on Vitamins B. E J Neurochem. 2016;103:425-438. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04773.x
- Fuentes J, Selva J, Moya C, Vázquez L, Lozano MV, Marcos P, Oliver M, Robledo V, Ortega MJ, González N, Jimenez MM. Neuroprotective Natural Molecules, From Food to Brain. Front Neurosci. 2018 Oct 23;12:721. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00721. PMID: 30405328; PMCID: PMC6206709.
- Wang X, Michaelis EK. Selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress in the brain. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010 Mar 30;2:12. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00012. PMID: 20552050; PMCID: PMC2874397.
- Santos LF, Freitas RL, Xavier SM, Saldanha GB, Freitas RM. Neuroprotective actions of vitamin C related to decreased lipid peroxidation and increased catalase activity in adult rats after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Mar;89(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.10.007. Epub 2007 Oct 23. PMID: 18096215.
- Aumailley L, Warren A, Garand C, Dubois MJ, Paquet ER, Le Couteur DG, et al. Vitamin C modulates the metabolic and cytokine profiles, alleviates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress, and increases the life span of Gulo-/- mice. Aging 8. 2016;458-483. doi: 10.18632/aging.10 0902
- Ramis MR, Sarubbo F, Terrasa JL, Moranta D, Aparicio S, Miralles A, et al. Chronic alpha-tocopherol increases central monoamines synthesis and improves cognitive and motor abilities in old rats. Rejuvenation Res. 2016;19:159-171. doi: 10.1089/rej.2015.1685
- Sun Y, Pham AN, Waite TD. The effect of vitamin C and iron on dopamine-mediated free radical generation: implications to Parkinson’s disease. Dalton Trans. 2018 Mar 28;47(12):4059-4069. doi: 10.1039/c7dt04373b. Epub 2018 Feb 6. PMID: 29406547.
- Rinaldi P, Polidori MC, Metastasio A, Mariani E, Mattioli P, Cherubini A, Catani M, Cecchetti R, Senin U, Mecocci P. Plasma antioxidants are similarly depleted in mild cognitive impairment and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003 Nov;24(7):915-919. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(03)00031-9. PMID: 12928050.
- Mangialasche F, Xu W, Kivipelto M, Costanzi E, Ercolani S, Pigliautile M, Cecchetti R, Baglioni M, Simmons A, Soininen H, Tsolaki M, Kloszewska I, Vellas B, Lovestone S, Mecocci P; AddNeuroMed Consortium. Tocopherols and tocotrienols plasma levels are associated with cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging. 2012 Oct;33(10):2282-2290. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.11.019. Epub 2011 Dec 20. PMID: 22192241.
- Petersen RC, Thomas RG, Grundman M, Bennett D, Doody R, Ferris S, Galasko D, Jin S, Kaye J, Levey A, Pfeiffer E, Sano M, van Dyck CH, Thal LJ; Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Group. Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. N Engl J Med. 2005 Jun 9;352(23):2379-88. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050151. Epub 2005 Apr 13. PMID: 15829527.
- Goodman M, Bostick RM, Kucuk O, Jones DP. Clinical trials of antioxidants as cancer prevention agents: past, present, and future. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Sep 1;51(5):1068-1084. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 May 24. PMID: 21683786.
- Santilli F, D’Ardes D, Davi, G. Oxidative stress in chronic vascular disease: from prediction to prevention. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015;74:23–37. doi: 10. 1016/j.vph.2015.09.003
- Basambombo LL, Carmichael PH, Côté S, Laurin D. Use of Vitamin E and C Supplements for the Prevention of Cognitive Decline. Ann Pharmacother. 2017 Feb;51(2):118-124. doi: 10.1177/1060028016673072. Epub 2016 Oct 5. PMID: 27708183.
- Monacelli F, Acquarone E, Giannotti C, Borghi R, Nencioni A. Vitamin C, aging and alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients. 2017 Jun 27;9(7):670. doi: 10.3390/nu9070670. PMID: 28654021; PMCID: PMC5537785.
- Ohlow MJ, Sohre S, Granold M, Schreckenberger M, Moosmann B. Why have clinical trials of antioxidants to prevent neurodegeneration failed? - A cellular investigation of novel phenothiazine-type antioxidants reveals competing objectives for pharmaceutical neuroprotection. Pharm Res. 2017 Feb;34(2):378-393. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-2068-0. Epub 2016 Nov 28. PMID: 27896592.
- Gueli N, Verrusio W, Linguanti A, Di Maio F, Martinez A, Marigliano B, et al. Vitamin D: drug of the future. A new therapeutic approach. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012;54(1):222-227. https://tinyurl.com/298dfb77
- Katouzian I, Jafari SM. Nano-encapsulation as a promising approach for targeted delivery and controlled release of vitamins. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2016;53:34-48.
- Bochicchio S, Barba AA, Grassi G, Lamberti G. Vitamin delivery: carriers based on nanoliposomes produced via ultrasonic irradiation, LWT. Food Sci Technol. 2016;69:9-16.
- Braithwaite MC, Kumar P, Choonara YE, du Toit LC, Tomar LK, Tyagi C. A novel multi-tiered experimental approach unfolding the mechanisms behind cyclodextrin-vitamin inclusion complexes for enhanced vitamin solubility and stability. Int J Pharm. 2017;532(1):90–104.
- Chaparro CM, Dewey KG. Use of lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNS) to improve the nutrient adequacy of general food distribution rations for vulnerable sub-groups in emergency settings. Matern Child Nutr. 2010 Jan;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):1-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8709.2009.00224.x. PMID: 20055936; PMCID: PMC6860843.
- Nutri-Facts: Understanding Vitamins & More. 2012. https://tinyurl.com/68yhwb9j
- Velikov KP, Pelan E. Colloidal Delivery Systems for Micronutrients and Nutraceuticals. Soft Matter. 2008;4:1964-1980.
- Gharsallaoui A, Roudaut G, Chambin O, Voilley, Saurel R. Applications of Spray-Dr ying in Microencapsulation of Food Ingredients: An Overview, Food Research International. 2007;40:1107-1121.
- Shahidi F, Han XQ. Encapsulation of food ingredients. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1993;33(6):501-547. doi: 10.1080/10408399309527645. PMID: 8216812.
- Gouin S. Microencapsulation: Industrial Appraisal of Existing Technologies and Trends. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2004;15:330-347.
- Kuang SS, Oliveira JC, Crean AM. Microencapsulation as a tool for incorporating bioactive ingredients into food. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2010 Nov;50(10):951-68. doi: 10.1080/10408390903044222. PMID: 21108075.
- Madene A, Jacquot M, Joël S, Desobry S. Flavour Encapsulation and Controlled Release- a Review. International Journal of Food Science and Technology. 2006;41:1-21.
- Augustin MA, Hemar Y. Nano- and micro-structured assemblies for encapsulation of food ingredients. Chem Soc Rev. 2009 Apr;38(4):902-912. doi: 10.1039/b801739p. Epub 2008 Dec 4. PMID: 19421570.
- Desai KGH, Park HJ. Recent Developments in Microencapsulation of Food Ingredients. Drying Technology. 2005;23:1361-1394.
- Annalisa D, Sabrina B, Gaetano L, Paolo B, Barbara J, Anna AB. Micronutrients encapsulation in enhanced nanoliposomal carriers by a novel preparative technology. RSC Adv. 2019;9:19800-19812. doi: 10.1039/c9ra03022k.
- Sreeraj G, Augustine A, Józef TH, Sabu T. Introduction of Nanotechnology in Herbal Drugs and Nutraceutical. A Review. J Nanomedine Biotherapeutic Discov. 2016 ;6:2 doi: 10.4172/2155-983X.1000143.
- Kingston DG. Modern natural products drug discovery and its relevance to biodiversity conservation. J Nat Prod. 2011 Mar 25;74(3):496-511. doi: 10.1021/np100550t. Epub 2010 Dec 7. PMID: 21138324; PMCID: PMC3061248.
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J Nat Prod. 2012 Mar 23;75(3):311-35. doi: 10.1021/np200906s. Epub 2012 Feb 8. PMID: 22316239; PMCID: PMC3721181.
- Bilia AR, Bergonzi MC, Guccione C, Manconi M, Fadda AM, et al. Sinico C: Vesicles and micelles. Two versatile vectors for the delivery of natural products. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec.
- Ajazuddin, Saraf S. Applications of novel drug delivery system for herbal formulations. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):680-689. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 May 12. PMID: 20471457.
- Shi F, Zhang Y, Yang G, Guo T, Feng N. Preparation of a micro/nanotechnology based multi-unit drug delivery system for a Chinese medicine Niuhuang Xingxiao Wan and assessment of its antitumor efficacy. Int J Pharm. 2015 Aug 15;492(1-2):244-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.07.023. Epub 2015 Jul 15. PMID: 26188318.
- Israeli-Lev G, Livney YD Self-assembly of hydrophobin and its coassembly with hydrophobic nutraceuticals in aqueous solutions. Towards application as delivery systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2014;35:28-35.
- Masiá R, Nicolás R, Periago MJ, Ros G, Lagaron JM, Rubio A. Encapsulation of folic acid in food hydrocolloids through nanospray drying and electrospraying for nutraceutical applications. Food Chem. 2015 Feb 1;168:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.051. Epub 2014 Jul 14. PMID: 25172691.
- Zaragoza ML, Silva E, Cortez E, Tostado E, Guerrero D. Optimization of nanocapsules preparation by the emulsion-diffusion method for food applications. LWT - Food Sci Technol. 2011;44:1362-1368. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2010.10.004
- Abbasi A, Emam-Djomeh Z, Mousavi MA, Davoodi D. Stability of vitamin D(3) encapsulated in nanoparticles of whey protein isolate. Food Chem. 2014 Jan 15;143:379-383. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.018. Epub 2013 Aug 12. PMID: 24054255.
- Kim T, Oh J. Dual nutraceutical nanohybrids of folic acid and calcium containing layered double hydroxides. J Solid State Chem. 2016;233:125-132. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2015.10.019
- Hosseini SMH, Djomeh Z, Sabatino P, Meeren P. Nanocomplexes arising from protein-polysaccharide electrostatic interaction as a promising carrier for nutraceutical compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2015;50:16-26.
- Lacatusu I, Badea N, Niculae G, Bordei N, Stan R. Lipid nanocarriers based on natural compounds: An evolving role in plant extract delivery. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol. 2014;116:1708-1717.
- Zhou H, Liu G, Zhang J, Sun N, Duan M, Yan Z, Xia Q. Novel lipid-free nanoformulation for improving oral bioavailability of coenzyme Q10. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:793879. doi: 10.1155/2014/793879. Epub 2014 Jun 5. PMID: 24995328; PMCID: PMC4068099.
- Cho HT, Trujillo L, Kim J, Park Y, Xiao H, McClements DJ. Droplet size and composition of nutraceutical nanoemulsions influences bioavailability of long chain fatty acids and Coenzyme Q10. Food Chem. 2014 Aug 1;156:117-122. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.084. Epub 2014 Feb 6. PMID: 24629946.
- Matalanis A, Jones OG, McClements DJ. Structured biopolymerbased delivery systems for encapsulation, protection, and release of lipophilic compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011;25:1865-1880.
- Yu H, Huang Q. Improving the oral bioavailability of curcumin using novel organogel-based nanoemulsions. J Agric Food Chem. 2012 May 30;60(21):5373-9. doi: 10.1021/jf300609p. Epub 2012 May 16. PMID: 22506728.
- Campardelli R, Reverchon E. α-Tocopherol nanosuspensions produced using a supercritical assisted process. J Food Eng. 2015;149:131-136.
- Yang W, Xu C, Liu F, Yuan F, Gao Y. Native and thermally modified protein-polyphenol coassemblies: lactoferrin-based nanoparticles and submicrometer particles as protective vehicles for (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Nov 5;62(44):10816-27. doi: 10.1021/jf5038147. Epub 2014 Oct 21. PMID: 25310084.
- Al-Okbi SY, Mohamed DA, Hamed TE, Edris AE. Protective effect of clove oil and eugenol microemulsions on fatty liver and dyslipidemia as components of metabolic syndrome. J Med Food. 2014 Jul;17(7):764-771. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.0033. Epub 2014 Mar 10. PMID: 24611461.
- Semyonov D, Ramon O, Shoham Y, Shimoni E. Enzymatically synthesized dextran nanoparticles and their use as carriers for nutraceuticals. Food Funct. 2014 Oct;5(10):2463-2474. doi: 10.1039/c4fo00103f. Epub 2014 Aug 11. PMID: 25110170.
- Hsu CY, Wang PW, Alalaiwe A, Lin ZC, Fang JY. Use of Lipid Nanocarriers to Improve Oral Delivery of Vitamins. Nutrients. 2019 Jan 1;11(1):68. doi: 10.3390/nu11010068. PMID: 30609658; PMCID: PMC6357185.
- Ventola CL. Progress in Nanomedicine: Approved and Investigational Nanodrugs. P T. 2017 Dec;42(12):742-755. PMID: 29234213; PMCID: PMC5720487.
- Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF, Campos, Torres, Torres LS, Torres LA, Grillo R, Swamy MK, Sharma S, Habtemariam S, Shin HS. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Sep 19;16(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8. PMID: 30231877; PMCID: PMC6145203.
- Maniam G, Mai CW, Zulkefeli M, Dufès C, Tan DMY, Fu JY. Challenges and opportunities of nanotechnology as delivery platform for tocotrienols in cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1358. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01358.
- Mario Pagliaro. Italy’s nutraceutical industry: A process and bioeconomy perspective into a key area of the global economy. © 2019 Society of Chemical Industry and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd | Biofuels, Bioprod. Bioref. 2020;14:180-186. doi: 10.1002/bbb.2059.
- Santini A, Novellino E. Nutraceuticals - shedding light on the grey area between pharmaceuticals and food. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;11(6):545-547. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1464911. Epub 2018 Apr 23. PMID: 29667442.
- FDA Guidance for industry: assessing the effects of significant manufacturing process changes, including emerging technologies, on the safety and regulatory status of food ingredients and food contact substances, including food ingredients that are color additives. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition. 2014. https://tinyurl.com/v9fmv77h
- Pagliaro M, Chemistry education fostering creativity in the digital era. Isr J Chem. 2019;59:565-571.
- Resende D, Lima SA, Reis S. Nanoencapsulation approaches for oral delivery of vitamin A. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Sep;193:111121. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111121. Epub 2020 May 15. PMID: 32464354.
- Chaudhry Q, Castle L. Food applications of nanotechnologies: An overview of opportunities and challenges for developing countries. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2011;22:595-603.
- Bucheli T Agricultural applications of nanotechnology. In: Parisi C, Vigani M, Cerezo E (eds) Proceedings of a workshop on Nanotechnology for the agricultural sector: from research to the field, Seville, November 2013. European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Prospective Technological Studies, Luxembourg. 214.
Content Alerts
SignUp to our
Content alerts.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.