Medicine Group . 2022 November 28;3(11):1404-1407. doi: 10.37871/jbres1612.
Effects of the Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medical Prescription-Yiqihuoxue Formula on Vasculopathy with Systemic Sclerosis
Yiyun Xue and Yinhuan Zhao*
- The prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula
- Vasculopathy
- Systemic sclerosis
- Traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
Vasculopathy is a prevalent complication that may appear in the early stage of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc). Traditional Chinese medical prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula (YQHX) has been used as a therapeutic option for SSc in our department, which has acquired a significant treatment effect. We interrogated the role of the YQHX on Vasculopathy with SSc by investigating its effects on the HDMECs from H2O2 injury. The viability of the HDMECs which were induced by H2O2 and then impacted by the YQHX was noticeably more than that of the H2O2-induced HDMECs, while the apoptosis cell percentage was significantly lower. The YQHX could promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis which meant it could protect HDMECs from H2O2 injury. And the tube formation assay shown that the YQHX may have a promoted effects on angiogenic properties of HDMECs. Our data demonstrated that the YQHX is helpful on alleviating vasculopathy. These data help in directing personalized therapeutic approaches in SSc.
Introduction
Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by functional and structural vasculopathy, dysimmunity and fibrosis of the skin and internal organs [1,2]. Although the pathogenesis of SSc remains elusive, it is generally accepted that vasculopathy and immune activation lead to activation of fibroblasts and fibrosis as the end effect [3]. The initial clinical situation of SSc is mostly Raynaud's Phenomenon (RP) caused by microvascular abnormalities, and most SSc patients show a very characteristic combination of capillary abnormalities [4]. The damage of internal organs such as pulmonary hypertension, heart failure and renal crises [5] may occur early or late in the disease course. These internal organ complications, especially pulmonary and cardiac involvement, cause morbidity and premature death in SSc [6]. To date, therapeutic options of many SSc patients are limited that treatment with immunosuppression can increase quality of life, decrease progression of organ involvement and increase survival [7,8].
The Traditional Chinese Medicine on SSc
In diagnostics of traditional Chinese medicine, SSc has been regarded as the impediment disease related to immune function. A growing body of evidences has pointed that traditional Chinese medicine has multiple roles in the treatment of systemic sclerosis [9]. The patient with SSc treated with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine showed ideal therapeutic effects in controlling the progression of the disease and improving symptoms [10]. In our department, the traditional Chinese medical prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula (YQHX) has been used to relieve the affection including vascular compromise, inflammation and fibrosis of SSc nearly 20 years, which has acquired a significant treatment effect [11].
The YQHX is composed of 10 herbs, including Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae (Danshen in Chinese), Radix Astragali (Huangqi in Chinese), Angelica Sinensis (Danggui in Chinese), Caulis Spatholobi (Fuling in Chinese), Peach Kernel (Taoren in Chinese), ,em>Szechuan Lovage Rhizome
(Chuanxiong in Chinese), Radix Rehmaniae Recens (Shudihuang in Chinese), Hedyotis Diffusa (Baihuasheshecao in Chinese), Herba Epimedii (Yinyanghuo in Chinese) and Eupolyphaga Seu Steleophaga (Tubiechong in Chinese). The 10 herbs complement each other to achieve the therapeutic effects. Studies have been found that Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae (Danshen in Chinese) and Radix Astragali (Huangqi in Chinese), as the monarch medicine of the YQHX, have positive effects on alleviating vasculopathy in SSc. Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae (Danshen in Chinese) could reduce intracellular as well as intravascular oxidative stress, which protects endothelial cells from free radical damage and peroxidation [12]. It can also attenuate H2O2-induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells [13]. And Radix Astragali (Huangqi in Chinese) could ameliorate H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury [14].This article mainly researched the effect of the mechanism of the YQHX on vasculopathy in SSc, which could provide future clinical guidance in the therapeutic options for SSc patients.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
Human Dermal Micro-Vascular Endothelial Cells (HDMECs) were obtained from Shanghai Dongjian Biotechnology Center. Cells were cultured in Endothelial Cell Medium (ECM) at 37°C under a humidified 5% (v/v) CO2 atmosphere and the medium was renewed every 1 or 2 days. Adherent cells were detached by treatment with phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.2, 0.02% (w/v) EDTA, 0.25% (w/v) trypsin.
Construction of cellular model
We used the non-interventional HDMECs as a blank group, the HDMECs from H2O2 injury as a control group [13]. And the experimental group would be the HDMECs induced by H2O2 and then impacted by the YQHX.
Preparation of the prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula
The granules of the YQHX (Neo-Green Pharmaceutical Technology Development Co., Ltd., Sichuan) were dissolved in distilled water to obtain a made-up liquid with a higher concentration, which would be placed at 4°C, and dilute when using.
The toxicity of the prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula
We determined the dosage of the YQHX with Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8, Beyotime biotechnology, Shanghai). The HDMECs were cultured in 96-well plates with different concentrations of the YQHX and Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM), and CCK-8 were applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was measured at 450nm by SpectraMax ID 3 (Molecular Devices, USA) as the result. The cell viability was calculated according to the formula: cell viability (%) = average A450 nm of the treated group/average A450 nm of the distilled-water group*100%. Each experiment was performed in quadruplicate and repeated at least three times.
Cell proliferation assay
The effect of the YQHX on cell proliferation were measured using CCK-8 too. The blank group, the control group and the experimental group were cultured in 96-well plates with DMEM, and CCK-8 were applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was measured as above. The cell viability was calculated as above. Each experiment was performed in quadruplicate and repeated at least three times.
Cell apoptosis assay
The effect of the YQHX on cell apoptosis were measured using AnnexinV-FITC/PI Apoptosis Assay Kit (Sunbio Technology, Nanjing). The blank group, the control group and the experimental group were cultured in 6-well plates with (DMEM, and AnnexinV-FITC/PI Apoptosis Assay Kit were applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The result of apoptosis assay was measured at Ex = 488 nm and Em = 530nm by FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences, USA). Each experiment was performed in quadruplicate and repeated at least three times.
Tube formation assay
The effect of the YQHX on angiogenic properties was measured using Matrigel Basement Membrane Matrix (BD Biosciences, USA). The blank group, the control group and the experimental group were cultured in 96-well plates with DMEM and Matrigel Basement Membrane Matrix was applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The tube formation was observed under Leica DMi8 (Leica, German) and the result was photographed by Leica DFC310FX (Leica, German). Each experiment was performed in quadruplicate and repeated at least three times.
Statistical analysis
All data were presented as with at least three independent experiments, each performed at least in triplicate. One-way analysis of variance was used to determine the statistical significance between different groups. Means were compared using Student’s t-tests, and p < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant. All data were analyzed with SPSS 25.0 and GraphPad Prism 8 software.
Results
The appropriate dosage of the prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula
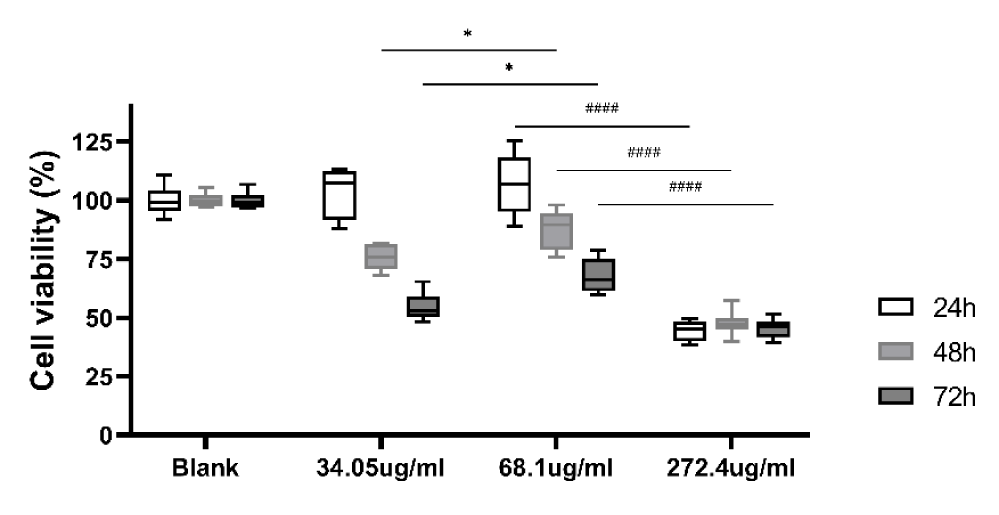
To determine the appropriate dosage of the YQHX, HDMECs were cultured in 96-well plates with different concentrations of the YQHX and DMEM. As shown in figure 1, after 24 h, the rate of cell viability in the group of the 68.1 ug/ml-YQHX (107.07 ± 12.46)% was significantly higher than that in the 272.4ug/ml-group (44.49 ± 4.52)%. After 48 h, the rate of cell viability in the 68.1 ug/ml-group (87.98 ± 8.36)% was higher than that in the 34.05 ug/ml-group (75.71 ± 5.37)%. After 72h, the rate of cell viability in the 68.1 ug/ml-group (67.80 ± 7.32)% was higher than that in the groups of other concentrations of the YQHX. In summary, the YQHX with the concentration of 68.1 ug/ml was less toxic to HDMECs, and the appropriate dosage of the YQHX would be 68.1 ug/ml in latter assays.
Effects of the prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula on proliferation and apoptosis of HDMECs
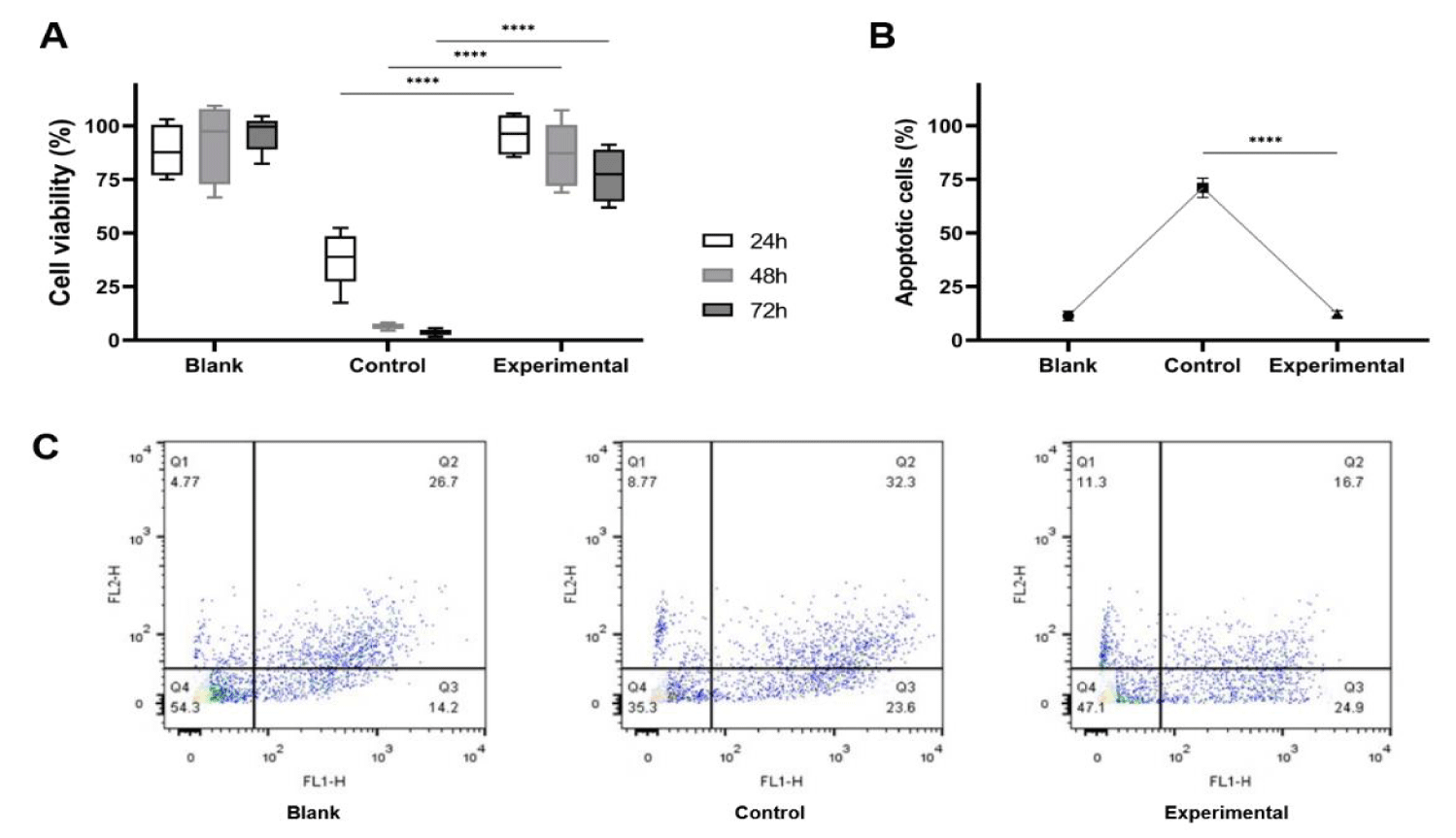
In order to verify the protective role of the YQHX for the HDMECs from H2O2 injury, we compared the cell proliferation and apoptosis in different groups including the blank group, the control group and the experimental group. The CCK-8 results showed that proliferation was promoted significantly in cells of the experimental group as compared with that of the control group. The rate of cell viability in the experimental group (86.68 ± 9.59)% was remarkably higher than that in control group (15.93 ± 18.86)% (Figure 2A). Consistent with cell proliferation assay results, the YQHX could inhibit apoptosis in HDMECs from H2O2 injury (Figure 2B); the apoptosis cell percentage in the experimental group (12.34 ± 1.37) was significantly lower than that in the control group (71.05 ± 4.53), but it was close to that in the blank group (11.33 ± 2.22). Taken together, these results indicated that the YQHX could promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis which meant it could protect HDMECs from H2O2 injury.
Effects of the prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula on angiogenic properties of HDMECs
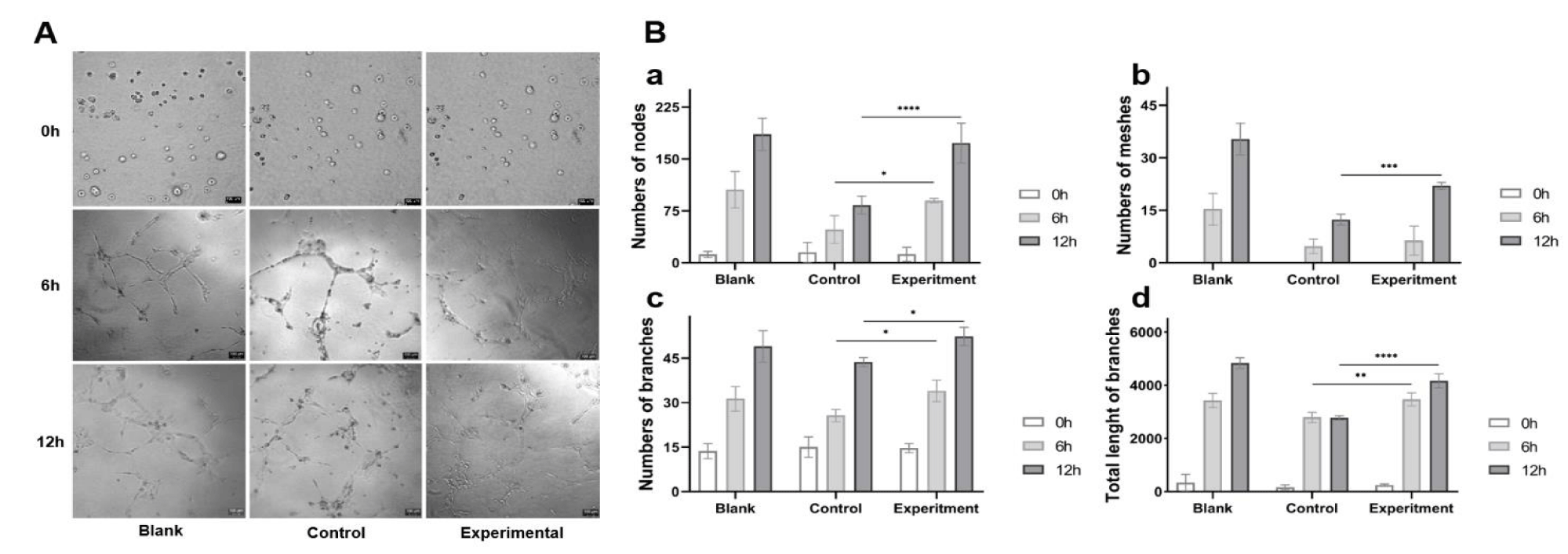
To investigate the effect of the YQHX on the angiogenic ability of HDMECs, tube formation assay was utilized. As shown in figure 3Ba,c, after the HDMECs cultured on Matrigel Basement Membrane Matrix for 6h, numbers of nodes and branches of the cells in experimental group were more than that in the control group, while numbers of meshes and total length of branches of the cells in the experimental group were also significantly more than that in the control group after 12h (Figure 3Bb,c). These results suggested that the YQHX had a promoted effects on angiogenic properties of HDMECs from H2O2 injury.
Discussion
Microcirculation impairment and related vasculopathy are hallmarks of Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) which are usually thought to have a key role in the early pathogenesis [15,16]. Evidence suggests there is an early insult to the microvasculature, followed by an ongoing chronic process that can result in profound vascular damage in a subset of patients who develop severe events such Digital Ulcers (DU) and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) [17]. The extant therapy for vascular SSc is limited, especially at the less severe stages of vasculopathy. Previous clinical studies have verified that the prescription-Yiqihuoxue formula (YQHX) has a significant treatment effect of relieving the affection including vascular compromise, inflammation and fibrosis of SSc [11]. Therefore, we aimed to research the effect of the mechanism of traditional Chinese medical YQHX on vasculopathy in SSc.
Endothelial cells, as central constituents of the vascular system, play a key role in all aspects of vascular homeostasis [18]. It was found that incubation of endothelial cells with SSc-immune complexes results in modulation of several molecules involved in the cardinal scleroderma pathophysiological processes [19]. Based on that, our experiment mainly focused on effects of the YQHX on human dermal micro-vascular endothelial cells (HDMECs). We used HDMECs from H2O2 injury to simulate the damaged cells of vascular SSc. The YQHX could promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis. It shown that the YQHX could protect HDMECs from H2O2 injury.
In addition, we found the YQHX could promote the angiogenic ability of HDMECs from H2O2 injury which may involve the mechanism of the therapeutic on SSc by promoting angiogenic. The onset of pathophysiological processes in SSc results in impaired vascular homeostasis, because of which angiogenesis is dysregulated and efficient vascular recovery is impaired, while the damage of the vessels evolves progressively from early to late stages and is characterized by different morphological aspects [20,21]. In line with this, the YQHX was shown to alleviate Raynaud's Phenomenon (RP) and DU in our preliminary clinical study [11].
In summary, there were few reports in the literature on effects of the traditional Chinese medical YQHX on vasculopathy in SSc. This study provided that which associated with protecting HDMECs from H2O2 injury, and promoting the angiogenesis. The results of the study suggested that the YQHX could be of great help in the treatment on vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis. Further investigations are still needed to determine the mechanisms which the YQHX effects on vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis.
References
- Kowal-Bielecka O, Fransen J, Avouac J, Becker M, Kulak A, Allanore Y, Distler O, Clements P, Cutolo M, Czirjak L, Damjanov N, Del Galdo F, Denton CP, Distler JHW, Foeldvari I, Figelstone K, Frerix M, Furst DE, Guiducci S, Hunzelmann N, Khanna D, Matucci-Cerinic M, Herrick AL, van den Hoogen F, van Laar JM, Riemekasten G, Silver R, Smith V, Sulli A, Tarner I, Tyndall A, Welling J, Wigley F, Valentini G, Walker UA, Zulian F, Müller-Ladner U; EUSTAR Coauthors. Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Aug;76(8):1327-1339. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209909. Epub 2016 Nov 9. PMID: 27941129.
- Gabrielli A, Avvedimento EV, Krieg T. Scleroderma. The New England Journal Of Medicine. 2009;360(19):1989–2003.
- Asano Y, Sato S. Vasculopathy in scleroderma. Semin Immunopathol. 2015 Sep;37(5):489-500. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0505-5. Epub 2015 Jul 8. PMID: 26152638.
- Smith V, Herrick AL, Ingegnoli F, Damjanov N, De Angelis R, Denton CP, Distler O, Espejo K, Foeldvari I, Frech T, Garro B, Gutierrez M, Gyger G, Hachulla E, Hesselstrand R, Iagnocco A, Kayser C, Melsens K, Müller-Ladner U, Paolino S, Pizzorni C, Radic M, Riccieri V, Snow M, Stevens W, Sulli A, van Laar JM, Vonk MC, Vanhaecke A, Cutolo M; EULAR Study Group on Microcirculation in Rheumatic Diseases and the Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium Group on Capillaroscopy. Standardisation of nailfold capillaroscopy for the assessment of patients with Raynaud's phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2020 Mar;19(3):102458. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102458. Epub 2020 Jan 10. PMID: 31927087.
- Chifflot H, Fautrel B, Sordet C, Chatelus E, Sibilia J. Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis: a systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Feb;37(4):223-35. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 Aug 9. PMID: 17692364.
- Truchetet ME, Brembilla NC, Chizzolini C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021 Sep 6. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08889-8. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34487318.
- Smeets RL, Kersten BE, Joosten I, Kaffa C, Alkema W, Koenen HJPM, Vonk MC. Diagnostic profiles for precision medicine in systemic sclerosis; stepping forward from single biomarkers towards pathophysiological panels. Autoimmun Rev. 2020 May;19(5):102515. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102515. Epub 2020 Mar 12. PMID: 32173517.
- Khader A, Valiaveetil B, Nalini SD, George B, Sasidharanpillai S, Nazeer MMA, Manikath N. Effect of monthly cyclophosphamide pulses on skin sclerosis in systemic sclerosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021 Sep-Oct;87(5):728-731. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_796_19. PMID: 34379952.
- Hou YZ, Zhao GR, Yang J, Yuan YJ, Zhu GG, Hiltunen R. Protective effect of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Angelica sinensis on endothelial cell damage induced by hydrogen peroxide. Life Sci. 2004 Aug 20;75(14):1775-86. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.05.005. PMID: 15268976.
- Wang XH, Zhang JQ, Kong Q, Tu WZ, Chen LM, Zhao YH. Application of integrated traditional chinese and western medicine in treatment of systemic sclerosis: A case report. Explore (NY). 2022 Jun 7:S1550-8307(22)00077-5. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2022.06.001. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35697584.
- Dongdong C, Wenzhen T, Lei W, Jiaqian Z, Ling Y. Follow-up of long-term efficacy of comprehensive stage therapy of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of systemic scleroderma. Chinese Journal of Dermatology and Venereal Diseases of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. 2015,14(6):364-367.
- Ho JH, Hong CY. Salvianolic acids: small compounds with multiple mechanisms for cardiovascular protection. J Biomed Sci. 2011 May 11;18(1):30. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-30. PMID: 21569331; PMCID: PMC3113734.
- Chan P, Chen YC, Lin LJ, Cheng TH, Anzai K, Chen YH, Liu ZM, Lin JG, Hong HJ. Tanshinone IIA Attenuates H₂O₂ -induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(6):1307-19. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500966. PMID: 23227799.
- Han R, Tang F, Lu M, Xu C, Hu J, Mei M, Wang H. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jun;15(6):4027-4034. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6515. Epub 2017 Apr 26. PMID: 28487940; PMCID: PMC5436204.
- Allanore Y, Distler O, Matucci-Cerinic M, Denton CP. Review: Defining a Unified Vascular Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Feb;70(2):162-170. doi: 10.1002/art.40377. Epub 2018 Jan 22. PMID: 29145709.
- Morrisroe K, Hansen D, Stevens W, Sahhar J, Ngian GS, Hill C, Roddy J, Walker J, Proudman S, Nikpour M. Gastric antral vascular ectasia in systemic sclerosis: a study of its epidemiology, disease characteristics and impact on survival. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 May 10;24(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02790-1. PMID: 35538587; PMCID: PMC9087964.
- Mecoli CA, Perin J, Van Eyk JE, Zhu J, Fu Q, Allmon AG, Rao Y, Zeger S, Wigley FM, Hummers LK, Shah AA. Vascular biomarkers and digital ulcerations in systemic sclerosis: results from a randomized controlled trial of oral treprostinil (DISTOL-1). Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;39(4):1199-1205. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04863-0. Epub 2019 Dec 19. PMID: 31858338; PMCID: PMC8211019.
- Michiels C. Endothelial cell functions. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2003;196(3):430-443. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10333
- Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulation fosters angiogenesis and blunts myofibroblast-like features of systemic sclerosis endothelial cells. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), keac433. Advance online publication.
- Guiducci S, Giacomelli R, Cerinic MM. Vascular complications of scleroderma. Autoimmunity Reviews. 2007;6(8):520-523.
- Romano E, Rosa I, Fioretto BS, Giuggioli D, Manetti M, Matucci-Cerinic M. Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulation fosters angiogenesis and blunts myofibroblast-like features of systemic sclerosis endothelial cells. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022 Jul 28:keac433. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac433. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35900177.
Content Alerts
SignUp to our
Content alerts.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.