General Science. 2023 November 17;4(11):1582-1585. doi: 10.37871/jbres1833.
Growing Impacts of Robotization and Artificial Intelligence for a Global Need to Act Urgently in the Face of the Risks and Potential Damages that Accompany the Development of Human Societies
Boaz Wadawa*
- Development challenges
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Robotization
- Risks and damages
- Human
- Scientific and technical research
- Alert
- Impact
- Solution
- Society
Abstract
The major challenges in terms of development lead us to focus in this work on the identification and evaluation of the impacts due to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotization. It emerges that the results of scientific and technical research and development constitute the epicenter from which we could propose effective and lasting solutions aimed at reducing or controlling and eradicating the risks and possible damage caused by the digital revolution. and automation. Therefore, the urgency of rethinking the future of humanity and its modernized society challenges all humans and in particular all living forces throughout the world.
Social Impact
Increasingly, the world population and its States are facing major challenges such as security, demographic growth, food and energy shortages, climate change, health, education, respect for human rights, the economy, development or modernity programs etc. Faced with all these global challenges, great powers and emerging countries are resorting to and strongly recommending more effective, efficient, sustainable and rapid scientific and technical solutions such as robotization and Artificial Intelligence (AI) [1-3]. This particularly concerns the development of New Information and Communication Techniques (NICT) and robotization or the autonomy of work with or without human intervention. In terms of research, the main goal is to increase the dynamic and static performance of systems by relying on scientific and technical challenges such as: automatic or AI-based learning, reinforcement learning, optimization, control, robotics, computer vision, autonomous models and systems diagnostics. As a result, the applications of research and innovations will significantly contribute to the creation of powerful power plants, innovative service companies and automated factories, to provide effective solutions to global challenges. However, aware of their low industrialization, non-emerging countries and African states will immediately seize the niche development opportunities offered by the use of NICTs [2-6]. However, we generally encounter less and less or almost no research work which challenges, raises awareness, educates and proposes solutions which can make it possible to control and/or eradicate the risks and damages due to robotization and to the digital revolution. In addition, the risks, possible damage and its serious implications are often mentioned in a disparate manner and isunderstood and/or simply ignored in favor of the advantages offered by robotization and its intelligent services [4,7]. We can cite the few warning signs where the advantages of automation and AI have provoked and rather led to major threats for humans their societies and the environment. According to reports from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the countries of Asia, Europe and the Americas respectively are the main sources of job threats and industrial pollution due to robotization and A.I. [1,7]. Therefore, some studies on the elimination of jobs by machines claim that by 2030, between 400 and 800 million people could be replaced by this rapid increase in automation and AI [8]. In terms of comparing human and machine performance, AI based on programs like IBM Deep-Blue and AlphaGo managed to beat respectively the world chess champion, Garry Kasparov in 1997 and another world chess champion Go game, Lee Sedol in 2016 [9]. In addition, human or humanoid robots surprisingly continue to achieve high performances in athletics, in object search and in terms of the ability to develop human or dehumanizing sensational feelings, etc. [9,10]. Furthermore, the consequences of the Chernobyl accident and industrial pollution still constitute a real and dangerous threat to the environment and to human health [1,11,12]. Indeed, the prejudices of ordinary people regarding the performance of robotization which tends to supplant or replace humans are growing and perceptible. The latter will lead the work of Paolo Bory and the work of Baumgartner et al to focus on the study of collaboration conflicts between AI and human players, then between Robots/Cobots and factory workers respectively [6,9,13]. Therefore, the originality of the work that we propose in this paper aims at an in-depth, effective and succinct study of the impacts, implications and proposals for possible solutions that challenge every human being about the dangers and potential damage of the digital revolution and robotization. This work is presented as follows:
- The methodological part consists of graphically structuring the impacts, advantages and disadvantages of empowerment and digitalization on key sectors of development in countries around the world.
- The solution and implication section is devoted to proposing possible solutions aimed at reducing or eradicating the disadvantages due to empowerment and A.I.
- The last part is dedicated to the conclusion of the work.
Methodology
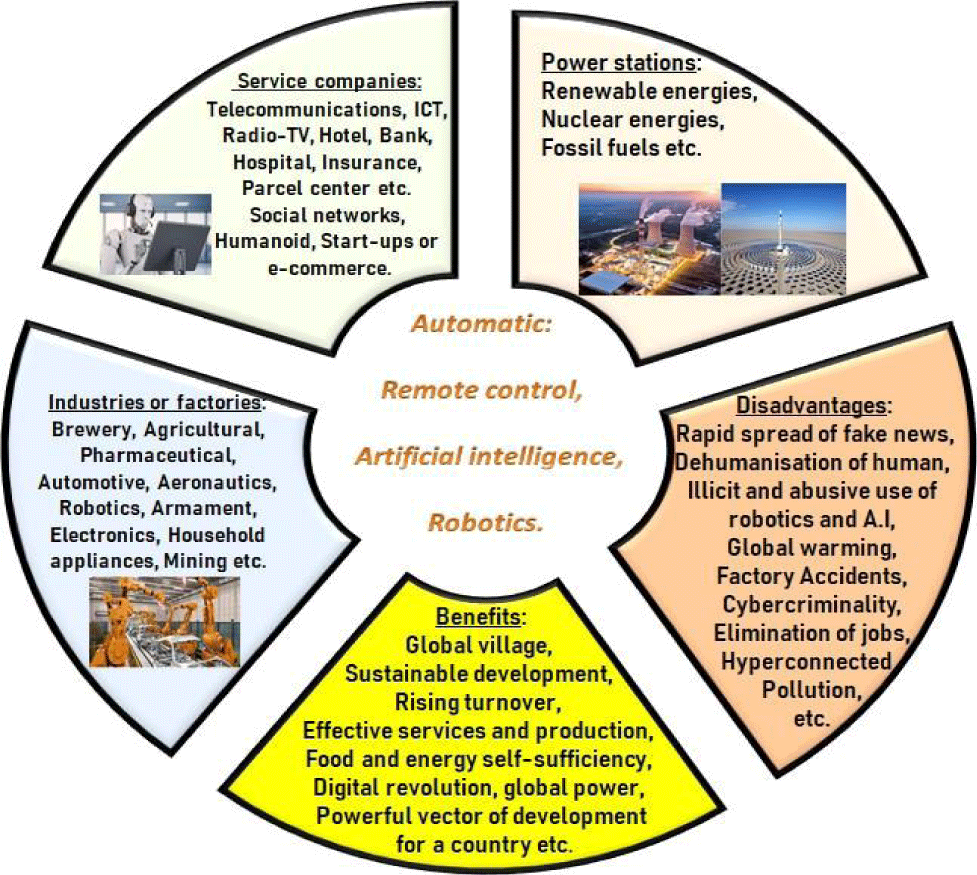
The graphic model that we propose in figure 1 allows us to illustrate a qualitative assessment of the influence of empowerment on the development of human societies. Specifically, the description in figure 1 aims to identify the advantages and disadvantages offered by the sectors of activity linked to robotization and digitalization. Firstly, we distinguish two categories of advantages according to the sectors of development. Innovative service companies present the advantages of a global village, creation and execution of tasks with Generative AI (GenAI) services or e-commerce services [5,14,15]. Then, the sustainable development of secure, efficient services thanks to the digital revolution in sectors such as: health, education and scientific and technical research, tourism, insurance, hotels, the field of transport, banking, telecommunications, etc [14,15]. Factories and power plants, for their part, offer the advantages of increased turnover, self-sufficiency with food and energy security, military security, production of quantity and quality, robots not affected by health crises, the exploitation of less polluting clean or non-renewable and/or mixed energies, etc [1-14]. Secondly, we can also group the disadvantages listed in figure 1 according to the sectors of development. The sector of service companies encompasses disadvantages such as hyper connection, cybercrime, the spread of fakes, the deterioration of relations between humans and the divine, massive job cuts and gluttony in terms of energy, hardware and data consumption, etc. While factories and power plants are the cause of pollution, job losses, the release into nature of toxic or radioactive waste, factory accidents, increased demand for energy, global warming, ecological problems due to exploitation illicit minerals, geopolitical conflicts due to inequitable sharing of resources, etc.
Results and Implications
Table 1 is a summary of the proposed solutions aimed at reducing, controlling and/or eradicating the risks and damages due to the implications of the disadvantages caused by robotization and the digital revolution. It emerges from table 1 that scientific and technical research and development must be at the heart of proposed solutions to reduce or stop the risks and/or possible damage caused by the rise of automation and A.I. in our modern societies. Furthermore, spiritual, ontological or philosophical, economic, traditional or cultural and legislative solutions will be added to science and technology for the preservation of human life and the control of human-machine coexistence.
| Table 1: Possible solutions linked to the disadvantages or risks and damages due to robotization and A.I. | ||
| Disadvantages | Implications | Possible solutions |
| Atmospheric pollution | Global warming Disrupts the climate and threatens health |
Reduction of CO2 propagation Intensify the development of clean energy |
| Nuclear accidents Emissions of toxic or radioactive waste |
Disaster or poisoning of humans and the environment | Cutting-edge control science and technology Techniques for efficient waste management, recycling and treatment |
| Illicit exploitation of natural resources | Rapid depletion of resources Ecological disasters Resource management conflicts |
Promote sustainable exploitation of resources Creation of environmental preservation tools and commissions Creation of conflict management funds with audits |
| Hyper connected | Burnout | Education for attention and humanism |
| Cybercrime | Internet scam | Permanent security of systems, data and applications |
| Uncontrolled proliferation of media or content on internet Uncontrolled genAI |
Spread of fakes ChatGPT, Large Language Model (LLM), Midjourney or Dall-e, Latext etc. [3, 14, 15] |
Creation of accreditations and authentication units for media or internet content GenAI must follow a design, authentication, use and security protocol based on ethics and respect for privacy. |
| Abusive robotization of service companies or excessive use of humanoid AI | Powerful digital colonization tool Elimination of service jobs Threat of human extinction Strong violation of human rights according to the UN charter [16] Isn't the humanoid AI the image of the beast that will demand the death of men rebellious to the act of idolatry, according to Revelation 13:15-18 of the Bible? [17] War robots or terrorist robots AI gluttony in hardware, data and energy Conflicts between Humans and Cobots in SME |
Urgent creation of research centers and AI applications in all countries Economic redistribution, distribution of value chains and creation of more qualified jobs for men Training and awareness on the risks and damages of AI Strengthening international laws of humans and robots (counting Asimov's three laws) [18]. The Bible in Genesis 11 advocates a “Tower of Babel” solution as an idea to confuse or control Robots (Solution via modeling and learning of Robots) Creation of hi-tech defense security centers based on AI Technical specifications underlying all AI/Robots Humanization and control of Cobots/Robots. |
Conclusion
Aware of the global challenges linked to the development of key sectors such as power plants, service companies and factories, we were interested in this work in the identification and evaluation of the impacts due to artificial intelligence (A.I) and robotization. It emerges that the results of scientific and technical research and development constitute the epicenter from which we could propose effective and lasting solutions aimed at reducing or eradicating the risks and damage possibly caused by the digital revolution and automation. . Therefore, it is urgent to raise awareness and challenge all the active forces in the world, with a view to rethinking the future of humanity and its modernized society.
References
- https://ifr.org/free-downloads/ (Consulted on 10/28/2023).
- BONJAWO, Jacques. Révolution numérique dans les pays en développement: l'exemple africain. Dunod. 2011.
- https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/fr/ (Consulted on, 11/18/2023).
- ASHTA, Arvind et MOGHA, Vipin. Les risques liés à l’innovation: Le cas de l’intelligence artificielle. Technol. Innov, 2023;8:1-14.
- DABBOUS, Amal, BARAKAT, Karine Aoun, et KRAUS, Sascha. The impact of digitalization on entrepreneurial activity and sustainable competitiveness: A panel data analysis. Technology in Society. 2023;73:102224. Doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102224.
- YEBOAH, Frederick Forkuo. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment: Evidence in Africa. Doi: 10.47772/IJRISS.2023.7487
- KHOGALI, Hisham O, MEKID Samir. The blended future of automation and AI: Examining some long-term societal and ethical impact features. Technology in Society. 2023;73:102232. Doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102232.
- BABAN, Elif. Les impacts de l'intelligence artificielle sur les employés dans le monde du travail. Mémoire de master. Université de Strasbourg. 2018.
- BORY P. Deep new: The shifting narratives of artificial intelligence from Deep Blue to AlphaGo. Convergence. 2019;25:627-642. Doi: 10.1177/1354856519829679.
- HÉRY, Michel. The effects of the automation of labor. Etudes. 2018;9:43-54.
- Mills-Knapp S, Traore K, Ericson B. The world’s worst pollution problems: Assessing health risks at hazardous waste sites. Blacksmith Institute, New York. 2012.
- Herndon J Marvin. La pollution atmosphérique est la cause principale du réchauffement climatique, pas les gaz à effet de serre. Journal of Geography, Environment and Earth Science International (JGEESI). 2018;17(2):1-8.
- Baumgartner, Marco, Kopp, Tobias, Kinkel, Steffen. Analysing factory workers’ acceptance of collaborative robots: a web-based tool for company representatives. Electronics. 2022:11:145. Doi: 10.3390/electronics11010145.
- https://fr.blog.businessdecision.com/chatgpt-midjourney-llm-mais-quest-ce-que-lia-generative/ (Consulted on, 11/18/2023)
- https://www.cyber.gc.ca/fr/orientation/lintelligence-artificielle-generative-itsap00041 (Consulted on, 11/18/2023)
- UNIES, Nations et PUYBARET, Eric. Déclaration universelle des droits de l'homme. Département de l'information de l'ONU, 2008.
- Segond, Louis. La Sainte Bible. [Bruxelles]: Société biblique. 1879.
- MACREZ, Franck. Les lois de la robotique d’Asimov, modèle pour le système juridique. 2020.
Content Alerts
SignUp to our
Content alerts.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.